Plant protein-based hydrophobic fine and ultrafine carrier particles in drug delivery systems
- PMID: 28434263
- PMCID: PMC5654697
- DOI: 10.1080/07388551.2017.1312267
Plant protein-based hydrophobic fine and ultrafine carrier particles in drug delivery systems
Abstract
For thousands of years, plants and their products have been used as the mainstay of medicinal therapy. In recent years, besides attempts to isolate the active ingredients of medicinal plants, other new applications of plant products, such as their use to prepare drug delivery vehicles, have been discovered. Nanobiotechnology is a branch of pharmacology that can provide new approaches for drug delivery by the preparation of biocompatible carrier nanoparticles (NPs). In this article, we review recent studies with four important plant proteins that have been used as carriers for targeted delivery of drugs and genes. Zein is a water-insoluble protein from maize; Gliadin is a 70% alcohol-soluble protein from wheat and corn; legumin is a casein-like protein from leguminous seeds such as peas; lectins are glycoproteins naturally occurring in many plants that recognize specific carbohydrate residues. NPs formed from these proteins show good biocompatibility, possess the ability to enhance solubility, and provide sustained release of drugs and reduce their toxicity and side effects. The effects of preparation methods on the size and loading capacity of these NPs are also described in this review.
Keywords: Plant; Sustained; delivery; drug; gliadin; lectin; legumin; nano-carrier; proteins; release; zein.
Figures


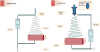


References
-
- Mofazzal Jahromi MA, Karimi M, Azadmanesh K, Naderi Manesh H, Hassan ZM, Moazzeni SM. The effect of chitosan-tripolyphosphate nanoparticles on maturation and function of dendritic cells. Comparative Clinical Pathology. 2014;23(5):1421–7.
-
- Karimi M, Zangabad PS, Ghasemi A, Hamblin MR. Smart Internal Stimulus-Responsive Nanocarriers for Drug and Gene Delivery. IOP Concise Physics. 2015
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
