Medial Entorhinal Cortex Selectively Supports Temporal Coding by Hippocampal Neurons
- PMID: 28434800
- PMCID: PMC5465388
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.04.003
Medial Entorhinal Cortex Selectively Supports Temporal Coding by Hippocampal Neurons
Abstract
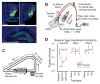
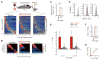
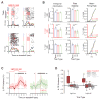
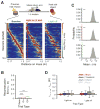
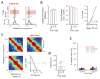
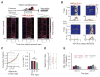
Recent studies have shown that hippocampal "time cells" code for sequential moments in temporally organized experiences. However, it is currently unknown whether these temporal firing patterns critically rely on upstream cortical input. Here we employ an optogenetic approach to explore the effect of large-scale inactivation of the medial entorhinal cortex on temporal, as well as spatial and object, coding by hippocampal CA1 neurons. Medial entorhinal inactivation produced a specific deficit in temporal coding in CA1 and resulted in significant impairment in memory across a temporal delay. In striking contrast, spatial and object coding remained intact. Further, we extended the scope of hippocampal phase precession to include object information relevant to memory and behavior. Overall, our work demonstrates that medial entorhinal activity plays an especially important role for CA1 in temporal coding and memory across time.
Keywords: CA1; hippocampus; medial entorhinal; memory; object selectivity; temporal coding; theta.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
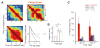

Similar articles
-
The medial entorhinal cortex is necessary for temporal organization of hippocampal neuronal activity.Nat Neurosci. 2015 Aug;18(8):1123-32. doi: 10.1038/nn.4056. Epub 2015 Jun 29. Nat Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26120964 Free PMC article.
-
Phase relations of theta oscillations in a computer model of the hippocampal CA1 field: Key role of Schaffer collaterals.Neural Netw. 2019 Aug;116:119-138. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2019.04.004. Epub 2019 Apr 8. Neural Netw. 2019. PMID: 31029053
-
Spatial coding and physiological properties of hippocampal neurons in the Cornu Ammonis subregions.Hippocampus. 2016 Dec;26(12):1593-1607. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22659. Epub 2016 Sep 27. Hippocampus. 2016. PMID: 27650887
-
A unified view of theta-phase coding in the entorhinal-hippocampal system.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2007 Apr;17(2):197-204. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2007.03.007. Epub 2007 Mar 26. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2007. PMID: 17379502 Review.
-
Allocentric representations of space in the hippocampus.Neurosci Res. 2020 Apr;153:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2019.06.002. Epub 2019 Jul 2. Neurosci Res. 2020. PMID: 31276699 Review.
Cited by
-
Neural Circuitry-Neurogenesis Coupling Model of Depression.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 28;22(5):2468. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052468. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33671109 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activity disruption causes degeneration of entorhinal neurons in a mouse model of Alzheimer's circuit dysfunction.Elife. 2022 Dec 5;11:e83813. doi: 10.7554/eLife.83813. Elife. 2022. PMID: 36468693 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal neurons represent events as transferable units of experience.Nat Neurosci. 2020 May;23(5):651-663. doi: 10.1038/s41593-020-0614-x. Epub 2020 Apr 6. Nat Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32251386 Free PMC article.
-
Phase precession in the human hippocampus and entorhinal cortex.Cell. 2021 Jun 10;184(12):3242-3255.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.04.017. Epub 2021 May 11. Cell. 2021. PMID: 33979655 Free PMC article.
-
Time Cells in the Hippocampus Are Neither Dependent on Medial Entorhinal Cortex Inputs nor Necessary for Spatial Working Memory.Neuron. 2019 Jun 19;102(6):1235-1248.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.04.005. Epub 2019 May 2. Neuron. 2019. PMID: 31056352 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chuong AS, Miri ML, Busskamp V, Matthews GA, Acker LC, Sorensen AT, Young A, Klapoetke NC, Henninger MA, Kodandaramaiah SB, Ogawa M, Ramanial SB, Bandler RC, Allen BD, Forest CR, Chow BY, Han X, Lin Y, Tye KM, Roska B, Cardin JA, Boyden ES. Noninvasive optical inhibition with a red-shifted microbial rhodopsin. Nature Neuroscience. 2014;17:1123–1129. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

