YM155 Down-Regulates Survivin and Induces P53 Up-Regulated Modulator of Apoptosis (PUMA)-Dependent in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells
- PMID: 28435150
- PMCID: PMC5412973
- DOI: 10.12659/msm.901643
YM155 Down-Regulates Survivin and Induces P53 Up-Regulated Modulator of Apoptosis (PUMA)-Dependent in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells
Abstract
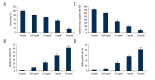
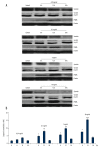
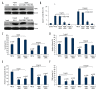
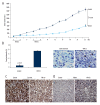
BACKGROUND YM155, which inhibits the anti-apoptotic protein survivin, is known to exert anti-tumor effects in various cancers. However, there were few reports describing the inhibitory effect of YM155 on human oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) cells that highly express survivin. In this study, we investigated the anti-tumor effects of YM155 on OSCC cells and then examined its molecular mechanisms. MATERIAL AND METHODS SCC9 cells of OSCC were treated with series of concentrations of YM155 (0.01, 0.1, 1, and 10 ng/ml) for 6, 12, and 24 h. The effect of YM155 on survival of SCC9 cells was detected by MTT and colony formation assay. Cell apoptosis was detected by flow cytometric analysis and the terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP-biotin nick-end labeling (TUNEL) assays. Western blot was used to detect the protein expression of survivin, p53, and PUMA. Caspase-3 activity was measured by cleavage of the caspase-3 substrate. To test the role of PUMA and caspase-3 on YM155-induced apoptosis and growth inhibition, the SCC9 cells was transfected with PUMA siRNA or caspase-3 siRNA or control siRNA for 16 h before YM155 (1 and 10 ng/ml) treatment for 24 h. In addition, we also investigated the effect of YM155 in an in vivo xenograft model. RESULTS Treatment of YM155 efficiently reduced survivin expression and increased PUMA expression and caspase-3 activation in the SCC9 cells. YM155 treatment resulted in 18-86% decrease in cell viability, 10-60% decrease in colony numbers, and 8-40% increase in cell apoptosis (p<0.05 and p<0.01). However, the induction of cell apoptosis growth inhibition was reversed by PUMA siRNA or caspase-3 transfection. In addition, animals treated with YM155 showed more than 60% tumor growth inhibition compared to the controls (p<0.05). CONCLUSIONS YM155 is a potent inhibitor of progression of SCC9 cells, which could be due to attenuation of survivin, and activation of the PUMA/caspase-3 cellular signaling processes. This study suggests that YM155 may be a potential molecular target with therapeutic relevance for the treatment of OSCC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting of Survivin Pathways by YM155 Inhibits Cell Death and Invasion in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;38(6):2426-37. doi: 10.1159/000445594. Epub 2016 Jun 13. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27287458
-
Dual induction of apoptotic and autophagic cell death by targeting survivin in head neck squamous cell carcinoma.Cell Death Dis. 2015 May 28;6(5):e1771. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.139. Cell Death Dis. 2015. PMID: 26018732 Free PMC article.
-
YM155 induces apoptosis through downregulation of specificity protein 1 and myeloid cell leukemia-1 in human oral cancer cell lines.J Oral Pathol Med. 2015 Nov;44(10):785-91. doi: 10.1111/jop.12299. Epub 2014 Dec 5. J Oral Pathol Med. 2015. PMID: 25475012
-
Survivin and YM155: how faithful is the liaison?Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Apr;1845(2):202-20. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2014.01.003. Epub 2014 Jan 16. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24440709 Review.
-
Research Progress of Metformin in the Treatment of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Endocrinology. 2023 Sep 23;164(11):bqad139. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqad139. Endocrinology. 2023. PMID: 37738154 Review.
Cited by
-
Benzyl isothiocyanate inhibits invasion and induces apoptosis via reducing S100A4 expression and increases PUMA expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2019 Apr 8;52(4):e8409. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X20198409. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2019. PMID: 30970087 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting survivin sensitizes cervical cancer cells to radiation treatment.Bioengineered. 2020 Dec;11(1):130-140. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2020.1717297. Bioengineered. 2020. PMID: 31959045 Free PMC article.
-
Dual targeting of Polo-like kinase 1 and baculoviral inhibitor of apoptosis repeat-containing 5 in TP53-mutated hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2020 Aug 28;26(32):4786-4801. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i32.4786. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32921957 Free PMC article.
-
Mitophagy-Related Gene CHDH Predicts Prognosis and Immune Response and Inhibits Proliferation and Migration in vitro and in vivo of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.J Inflamm Res. 2025 May 26;18:6831-6851. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S516427. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40453965 Free PMC article.
-
BIRC5 Is a Potential Biomarker Associated with Immune System Infiltration in Glioma.J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2025 Mar;68(2):184-201. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2024.0106. Epub 2025 Feb 26. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2025. PMID: 39999831 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kademani D. Oral cancer. Mayo Clin Proc. 2007;82:878–87. - PubMed
-
- Petersen PE. Oral cancer prevention and control – the approach of the World Health Organization. Oral Oncol. 2009;45:454–60. - PubMed
-
- Chen GS, Chen CH. A study on survival rates of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2006;12:317–25. - PubMed
-
- Lim YC, Choi EC. Surgery alone for squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity: survival rates, recurrence patterns, and salvage treatment. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2008;128:1132–37. - PubMed
-
- Deveraux QL, Reed JC. IAP family proteins – suppressors of apoptosis. Genes Dev. 1999;13:239–52. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

