Clinical and biochemical study of d-serine metabolism among schizophrenia patients
- PMID: 28435276
- PMCID: PMC5391825
- DOI: 10.2147/NDT.S126979
Clinical and biochemical study of d-serine metabolism among schizophrenia patients
Abstract
Background: Schizophrenia is a typical N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor (NMDA-R) hypofunction disorder. Decreased d-serine (d-Ser) levels in the periphery occur in schizophrenia and may reflect decreased availability of d-Ser to activate NMDA-R in the brain.
Objective: The objective of this study was to investigate the role of d-Ser metabolism in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia via biochemical assays and correlates, the serum level of d-Ser, d-serine racemase (SR) (responsible for its formation from l-serine [l-Ser]) and d-amino acid oxidase (DAAO) (responsible for its catabolism), among different clinical types of schizophrenia patients.
Patients and methods: This cross-sectional case-control study was carried out on 100 patients and 50 controls. They were recruited from the outpatients' psychiatric unit of the Neuropsychiatric Department of Assiut University Hospital, Upper Egypt. The type of schizophrenia was determined according to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition (DSM-IV), while the severity of schizophrenia was determined according to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5). Serum d-Ser levels were estimated using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), while serum SR and DAAO were measured using commercially available enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kits.
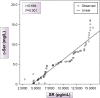
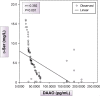
Results: There were significantly lower mean serum levels of d-Ser and SR and significantly higher mean serum levels of DAAO (P-value <0.01 for each) among schizophrenia patients when compared with the control group. Paranoid schizophrenia had the highest frequency, with a significantly lower serum levels of d-Ser and SR in the residual type and significantly higher serum levels of DAAO in undifferentiated and catatonic types. Combined receiver-operating characteristic curve for serum d-Ser, SR and DAAO indicated that the best serum level cutoff points at which schizophrenia manifestations started to appear were ≤ 61.4 mg/L for d-Ser, ≤ 15.5 pg/mL for SR and >35.6 pg/mL for DAAO.
Conclusion: The present study confirms that disturbed d-Ser metabolism could be implicated in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia.
Keywords: D-amino acid oxidase; D-serine; HPLC; schizophrenia; serine racemase.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Increased brain D-amino acid oxidase (DAAO) activity in schizophrenia.Schizophr Res. 2008 Apr;101(1-3):76-83. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2008.02.002. Epub 2008 Apr 2. Schizophr Res. 2008. PMID: 18378121
-
D-amino acid oxidase inhibitors as a novel class of drugs for schizophrenia therapy.Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(14):2499-511. doi: 10.2174/1381612811319140002. Curr Pharm Des. 2013. PMID: 23116391 Review.
-
Modulating NMDA Receptor Function with D-Amino Acid Oxidase Inhibitors: Understanding Functional Activity in PCP-Treated Mouse Model.Neurochem Res. 2016 Feb;41(1-2):398-408. doi: 10.1007/s11064-016-1838-8. Epub 2016 Feb 8. Neurochem Res. 2016. PMID: 26857796 Free PMC article.
-
Is rat an appropriate animal model to study the involvement of D-serine catabolism in schizophrenia? Insights from characterization of D-amino acid oxidase.FEBS J. 2011 Nov;278(22):4362-73. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08354.x. Epub 2011 Oct 10. FEBS J. 2011. PMID: 21981077
-
Drug discovery strategies and the preclinical development of D-amino-acid oxidase inhibitors as antipsychotic therapies.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2018 Oct;13(10):973-982. doi: 10.1080/17460441.2018.1524459. Epub 2018 Sep 22. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2018. PMID: 30220232 Review.
Cited by
-
Decreased free D-aspartate levels in the blood serum of patients with schizophrenia.Front Psychiatry. 2024 Jul 10;15:1408175. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1408175. eCollection 2024. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39050919 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and preliminary evaluation of 4-hydroxy-6-(3-[11C]methoxyphenethyl)pyridazin-3(2H)-one, a 11C-labeled d-amino acid oxidase (DAAO) inhibitor for PET imaging.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2020 Aug 15;30(16):127326. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2020.127326. Epub 2020 Jun 9. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2020. PMID: 32631531 Free PMC article.
-
L-serine: Neurological Implications and Therapeutic Potential.Biomedicines. 2023 Jul 27;11(8):2117. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11082117. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37626614 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances and challenges in serine in the central nervous system: physicochemistry, physiology, and pharmacology.Metab Brain Dis. 2024 Dec;39(8):1637-1647. doi: 10.1007/s11011-024-01418-4. Epub 2024 Aug 26. Metab Brain Dis. 2024. PMID: 39186223 Review.
-
Glycine Signaling in the Framework of Dopamine-Glutamate Interaction and Postsynaptic Density. Implications for Treatment-Resistant Schizophrenia.Front Psychiatry. 2020 May 14;11:369. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00369. eCollection 2020. Front Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32477178 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Collin L, Bindra J, Raju M, Gillberg C, Minnis H. Facial emotion recognition in child psychiatry: a systematic review. Res Dev Disabil. 2013;34(5):1505–1520. - PubMed
-
- Elvevag B, Goldberg TE. Cognitive impairment in schizophrenia is the core of the disorder. World Health Report 2001. Mental health: new understanding, new hope. Geneva: World Health Organization. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2000;14(1):1–21. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

