Subanesthetic ketamine for pain management in hospitalized children, adolescents, and young adults: a single-center cohort study
- PMID: 28435316
- PMCID: PMC5388303
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S131156
Subanesthetic ketamine for pain management in hospitalized children, adolescents, and young adults: a single-center cohort study
Abstract
Background: Subanesthetic doses of ketamine, an N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonist used as an adjuvant to opioid for the treatment of pain in adults with acute and chronic pain, have been shown, in some instances, to improve pain intensity and to decrease opioid intake. However, less is known about the role of ketamine in pain management in children, adolescents, and young adults.
Purpose: We examined the effects of subanesthetic ketamine on pain intensity and opioid intake in children, adolescents, and young adults with acute and chronic pain syndromes treated in an inpatient setting.
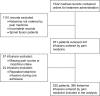
Methods: This is a longitudinal cohort study of patients treated with subanesthetic ketamine infusions in regular patient care units in a tertiary pediatric hospital. Primary outcomes included changes in pain scores and morphine-equivalent intake.
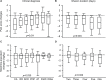
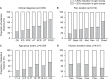
Results: The study cohort included 230 different patients who during 360 separate hospital admissions received subanesthetic ketamine infusions for pain management. Overall, ketamine infusions were associated with significant reductions in mean pain scores from baseline (mean pain scores 6.64 [95% CI: 6.38-6.90]) to those recorded on the day after discontinuation of ketamine (mean pain scores 4.38 [95% CI: 4.06-4.69]), p<0.001. Importantly, the effect of ketamine on pain scores varied according to clinical diagnosis (p=0.011), infusion duration (p=0.004), and pain location (p=0.004). Interestingly, greater reductions in pain scores were observed in patients with cancer pain and patients with pain associated with pancreatitis and Crohn's disease. There were no records of psychotomimetic side effects requiring therapy.
Conclusion: These data suggest that administration of subanesthetic ketamine for pain management is feasible and safe in regular inpatient care units and may benefit children, adolescents, and young adults with acute and chronic pain. This study is informative and can be helpful in determining sample and effect sizes when planning clinical trials to determine the role of subanesthetic ketamine infusions for pain management in pediatric patients.
Keywords: CRPS; acute pain; cancer pain; chronic pain; postoperative pain; sickle cell disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure This article was prepared while Zenaide MN Quezado, MD was employed at the Children’s National Health System. The opinions expressed in this article are the author’s own and do not reflect the view of the National Institutes of Health, the Department of Health and Human Services, or the United States government. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Corssen G, Miyasaka M, Domino EF. Changing concepts in pain control during surgery: dissociative anesthesia with CI-581. A progress report. Anesth Analg. 1968;47(6):746–759. - PubMed
-
- Mellon RD, Simone AF, Rappaport BA. Use of anesthetic agents in neonates and young children. Anesth Analg. 2007;104(3):509–520. - PubMed
-
- Finkel JC, Pestieau SR, Quezado ZM. Ketamine as an adjuvant for treatment of cancer pain in children and adolescents. J Pain. 2007;8(6):515–521. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

