Influence of daily oral prophylactic selenium treatment on the dibutyltin dichloride (DBTC)-induced pancreatitis in rats
- PMID: 28435430
- PMCID: PMC5379116
- DOI: 10.17179/excli2016-466
Influence of daily oral prophylactic selenium treatment on the dibutyltin dichloride (DBTC)-induced pancreatitis in rats
Abstract
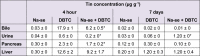
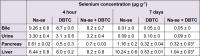
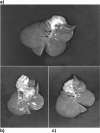
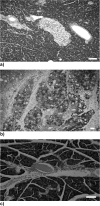
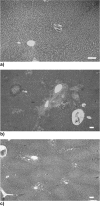
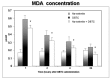
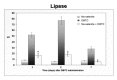
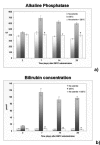
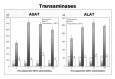
Dibutyltin dichloride (DBTC) is an organotin compound used as model for acute and chronic pancreatitis. Oxidative stress is one of the mechanisms of propagation of acinar cell injury in acute pancreatitis. Selenium is an essential cofactor in the antioxidant glutathione peroxidase pathway. Selenium levels are described to be subnormal in patients with acute and chronic pancreatitis. The aim of our studies was to determine the prophylactic effect of Na-selenite [5 mg kg-1 body weight (b.w.) per os (p.o.) 7 days] on the pathogenesis and course of DBTC- induced pancreatitis. Male inbred rats (LEW-1W Charles River) of 150 g body weight were used in this study. Experimental pancreatitis was induced by intravenous administration of 6 mg kg-1 b.w. DBTC in rats. Na-selenite was administered as daily oral dose of 5 mg kg-1 b.w. 7 days before induction of DBTC-pancreatitis. Malondialdehyde (MDA) was measured for monitoring levels of oxidative stress. Elimination of DBTC was reflected as tin concentration in bile and urine. Organ changes were indicated by serum parameters as well as histology. A prophylactic Na-selenite application significantly diminished MDA- and bilirubin concentration in serum, activities of lipase and transaminases as well as organ injuries compared to DBTC- treated rats in the absence of Na-selenite. The prophylactic oral treatment with Na-selenite in the scope of DBTC-induced pancreatitis points to a reduced oxidative stress characterized by diminished MDA serum levels and a milder course of pancreatitis suggesting prophylactic substitution with Na-selenite to probably elicit beneficial effect on the clinical outcome in patients with endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP).
Keywords: DBTC; acute pancreatitis; oxidative stress; selenium.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Influence of selenium treatment on the acute toxicity of dibutyltin dichloride in rats.Pancreatology. 2006;6(5):486-96. doi: 10.1159/000094666. Epub 2006 Jul 19. Pancreatology. 2006. PMID: 16864971
-
Acute interstitial pancreatitis in rats induced by dibutyltin dichloride (DBTC): pathogenesis and natural course of lesions.Pancreas. 1997 Nov;15(4):392-401. doi: 10.1097/00006676-199711000-00010. Pancreas. 1997. PMID: 9361094
-
The influence of ethanol on long-term effects of dibutyltin dichloride (DBTC) in pancreas and liver of rats.Hum Exp Toxicol. 1998 Mar;17(3):144-50. doi: 10.1177/096032719801700304. Hum Exp Toxicol. 1998. PMID: 9587782
-
Different characteristics of chronic dibutyltin dichloride-induced pancreatitis and cholangitis in mouse and rat.Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2020 Apr;19(2):169-174. doi: 10.1016/j.hbpd.2019.10.007. Epub 2019 Nov 22. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2020. PMID: 31919037
-
Oxidative stress in acute pancreatitis.Hepatogastroenterology. 1999 Sep-Oct;46(29):2736-50. Hepatogastroenterology. 1999. PMID: 10576339 Review.
Cited by
-
Selenium and zinc supplementation mitigates metals-(loids) mixture- mediated cardiopulmonary toxicity via attenuation of antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and antiapoptotic mechanisms in female Sprague Dawley rats.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2023 Dec 9;13(1):tfad119. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfad119. eCollection 2024 Feb. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2023. PMID: 38179003 Free PMC article.
-
The protective effects of selenium supplementation on ambient PM2.5-induced cardiovascular injury in rats.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018 Aug;25(22):22153-22162. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-2292-8. Epub 2018 May 26. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29804245
References
-
- Albrecht R, Pelissier MA, Boisset M. Excessive dietary selenium decreases the vitamin storage and the enzymatic antioxidant defence in the liver of rats. Toxicol Lett. 1994;70:291–297. - PubMed
-
- Barnes JM, Magee PN. The biliary and hepatic lesion produced experimentally by dibutyltin salts. J Path Bact. 1958;75:267–279. - PubMed
-
- Birk D, Schoenberg MH, Eisele S. Die Bedeutung der Sauerstoffradikale bei akuter Pankreatitis. Klinische und experimentelle Ergebnisse der Radikalfängertherapie. Med Klin. 1995;90:32–35. - PubMed
-
- Forceville X, Vitoux D, Gauzit R, Combes A, Lahilaire P, Chappuis P. Selenium, systemic immune response syndrome, sepsis, and outcome in critically ill patients. Crit Care Med. 1998;9:1536–1544. - PubMed
-
- Frommhold B, Merkord J, Paegelow I. Influence of selenium on the glutathione peroxidase in serum of rats with a pancreatitis induced by dibutyltin dichloride (DBTC) Naunyn Schmiedeberg´s Arch Pharmacol. 1997;356:243.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
