The Clinical Effectiveness of School Screening Programme for Idiopathic Scoliosis in Malaysia
- PMID: 28435573
- PMCID: PMC5393113
- DOI: 10.5704/MOJ.1703.018
The Clinical Effectiveness of School Screening Programme for Idiopathic Scoliosis in Malaysia
Abstract
Introduction: There is no large population size study on school screening for scoliosis in Malaysia. This study is aimed to determine the prevalence rate and positive predictive value (PPV) of screening programme for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis.
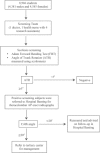
Materials and methods: A total of 8966 voluntary school students aged 13-15 years old were recruited for scoliosis screening. Screening was done by measuring the angle of trunk rotation (ATR) on forward bending test (FBT) using a scoliometer. ATR of 5 degrees or more was considered positive. Positively screened students had standard radiographs done for measurement of the Cobb angle. Cobb angle of >10° was used to diagnose scoliosis. The percentage of radiological assessment referral, prevalence rate and PPV of scoliosis were then calculated.
Results: Percentage of radiological assessment referral (ATR >5°) was 4.2% (182/4381) for male and 5.0% (228/4585) for female. Only 38.0% of those with ATR >5° presented for further radiological assessment. The adjusted prevalence rate was 2.55% for Cobb angle >10°, 0.59% for >20° and 0.12% for >40°. The PPV is 55.8% for Cobb angle >10°, 12.8% for >20° and 2.6% for > 40°.
Conclusions: This is the largest study of school scoliosis screening in Malaysia. The prevalence rate of scoliosis was 2.55%. The positive predictive value was 55.8%, which is adequate to suggest that the school scoliosis screening programme did play a role in early detection of scoliosis. However, a cost effectiveness analysis will be needed to firmly determine its efficacy.
Keywords: adolescent idiopathic scoliosis; positive predictive value; prevalence; school screening.
Figures
References
-
- Wong HK, Hui JH, Rajan U, Chia HP. Idiopathic scoliosis in Singapore schoolchildren: a prevalence study 15 years into the screening program. Spine. 2005;30(10):1188–1196. - PubMed
-
- Yong F, Wong HK, Chow KY. Prevalence of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis among female school children in Singapore. Ann Acad Med Singapore. 2009;38(12):1056–1063. - PubMed
-
- Luk KD, Lee CF, Cheung KM, Cheng JC, Ng BK, Lam TP, et al. Clinical effectiveness of school screening for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a large population-based retrospective cohort study. Spine. 2010;35(17):1607–1614. - PubMed
-
- Ueno M, Takaso M, Nakazawa T, Imura T, Saito W, Shintani R, et al. A 5-year epidemiological study on the prevalence rate of idiopathic scoliosis in Tokyo: school screening of more than 250,000 children. J Orthop Sci. 2011;16(1):1–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous