Crystal structure of O-benzyl-l-tyrosine N-carb-oxy anhydride
- PMID: 28435719
- PMCID: PMC5382620
- DOI: 10.1107/S2056989017004236
Crystal structure of O-benzyl-l-tyrosine N-carb-oxy anhydride
Abstract
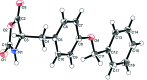
In the title compound, C17H15NO4 (alternative name; O-benzyl-l-tyrosine N-carb-oxy anhydride), the oxazolidine ring is planer, with an r.m.s. deviation of 0.039 Å. The benz-yloxy and benzyl rings are almost coplanar, making a dihedral angle of 0.078 (10)°, and are inclined to the oxazolidine ring by 59.16 (11) and 58.42 (11)°, respectively. In the crystal, mol-ecules are linked by N-H⋯O and C-H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming ribbons propagating along [010]. The ribbons are linked by C-H⋯π inter-actions, forming a three-dimensional supra-molecular structure. The oxazolidine rings of adjacent ribbons are arranged into a layer parallel to the ab plane. This arrangement is favourable for the polymerization of the compound in the solid state.
Keywords: C—H⋯π interactions; O-benzyl-l-tyrosine NCA; crystal structure; hydrogen bonding; l-amino acid N-carboxy anhydride; l-tyrosine; solid-state polymerization.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Crystal structure of γ-methyl l-glutamate N-carb-oxy anhydride.Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2015 Jan 1;71(Pt 1):48-50. doi: 10.1107/S2056989014026917. eCollection 2015 Jan 1. Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2015. PMID: 25705448 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of γ-ethyl-l-glutamate N-carb-oxy anhydride.Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2015 Jan 1;71(Pt 1):110-2. doi: 10.1107/S2056989014027170. eCollection 2015 Jan 1. Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2015. PMID: 25705466 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of β-benzyl dl-aspartate N-carb-oxyanhydride.Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2017 Feb 24;73(Pt 3):445-447. doi: 10.1107/S2056989017003024. eCollection 2017 Mar 1. Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2017. PMID: 28316828 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structures and anti-oxidant capacity of (E)-5-benz-yloxy-2-{[(4-chloro-phen-yl)imino]-meth-yl}phenol and (E)-5-benz-yloxy-2-({[2-(1H-indol-3-yl)eth-yl]iminium-yl}meth-yl)phenolate.Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2018 Mar 9;74(Pt 4):478-482. doi: 10.1107/S2056989018003687. eCollection 2018 Apr 1. Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2018. PMID: 29765750 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of (E)-4-{2-[4-(all-yloxy)phen-yl]diazen-yl}benzoic acid.Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2014 Nov 15;70(Pt 12):499-502. doi: 10.1107/S1600536814023745. eCollection 2014 Dec 1. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2014. PMID: 25552976 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Crisma, M., Valle, G., Formaggio, F., Toniolo, C. & Kamphui, J. (1995). Z. Kristallogr. 210, 634–635.
-
- Higashi, T. (1995). ABSCOR. Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
-
- Kanazawa, H. (2000). Acta Cryst. C56, 469–470. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
