Dual-Energy CT in Head and Neck Imaging
- PMID: 28435761
- PMCID: PMC5371622
- DOI: 10.1007/s40134-017-0213-0
Dual-Energy CT in Head and Neck Imaging
Abstract
Purpose of review: To explain the technique of Dual-energy CT (DECT) and highlight its applications and advantages in head and neck radiology.
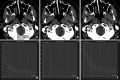
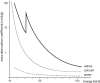
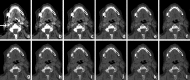
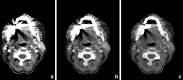
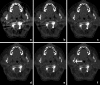
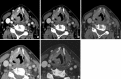
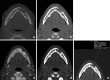
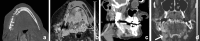
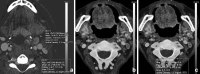
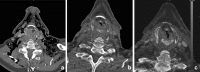
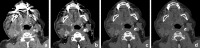
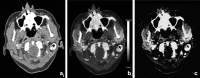
Recent findings: Using DECT, additional datasets can be created next to conventional images. In head and neck radiology, three material decomposition algorithms can be used for improved lesion detection and delineation of the tumor. Iodine concentration measurements can aid in differentiating malignant from nonmalignant lymph nodes and benign posttreatment changes from tumor recurrence. Virtual non-calcium images can be used for detection of bone marrow edema. Virtual mono-energetic imaging can be useful for improved iodine conspicuity at lower keV and for reduction of metallic artifacts and increase in signal-to-noise ratio at higher keV.
Summary: DECT and its additional reconstructions can play an important role in head and neck cancer patients, from initial diagnosis and staging, to therapy planning, evaluation of treatment response and follow-up. Moreover, it can be helpful in imaging of infections and inflammation and parathyroid imaging as supplementary reconstructions can be obtained at lower or equal radiation dose compared with conventional single energy scanning.
Keywords: Dual-energy CT; Head and neck cancer; Lymph node imaging; Metal artifact reduction; Parathyroid adenoma; Spectral CT.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
Elise D. Roele, Veronique C. M. L. Timmer, Lauretta A. A. Vaassen, and Anna M. J. L. van Kroonenburgh, all declare no potential conflicts of interest. A. A. Postma reports speaker fees from Bayer and is a section editor for
Human and Animal Rights
All reported studies/experiments with human or animal subjects performed by the authors have been previously published and complied with all applicable ethical standards (including the Helsinki declaration and its amendments, institutional/national research committee standards, and international/national/institutional guidelines).
Figures







References
-
- Watanabe Y, Uotani K, Nakazawa T, Higashi M, Yamada N, Hori Y, et al. Dual-energy direct bone removal CT angiography for evaluation of intracranial aneurysm or stenosis: comparison with conventional digital subtraction angiography. Eur Radiol. 2009;19(4):1019–1024. doi: 10.1007/s00330-008-1213-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Boll DT, Patil NA, Paulson EK, Merkle EM, Simmons WN, Pierre SA, et al. Renal stone assessment with dual-energy multidetector CT and advanced postprocessing techniques: improved characterization of renal stone composition–pilot study. Radiology. 2009;250(3):813–820. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2503080545. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bauer RW, Kerl JM, Weber E, Weisser P, Korkusuz H, Lehnert T, et al. Lung perfusion analysis with dual energy CT in patients with suspected pulmonary embolism–influence of window settings on the diagnosis of underlying pathologies of perfusion defects. Eur J Radiol. 2011;80(3):e476–e482. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2010.09.009. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
