Comparison of the behavior of CHO cells during cultivation in 24-square deep well microplates and conventional shake flask systems
- PMID: 28435799
- PMCID: PMC5381691
- DOI: 10.1016/j.btre.2014.04.001
Comparison of the behavior of CHO cells during cultivation in 24-square deep well microplates and conventional shake flask systems
Abstract
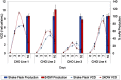
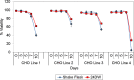
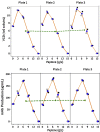
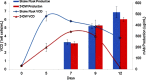
In biopharmaceutical production, the optimization of cell culture media and supplementation is a vital element of process development. Optimization is usually achieved through the screening of multiple media, feed and feeding strategies. However, most screening is performed in shake flasks, which makes the screening process very time consuming and inefficient. The use of small scale culture systems for the screening process can aid in the ability to screen multiple formulations during process development. In order to assess the suitability of 24 deep well (24DW) plates with the Duetz sandwich-covers as a small scale culture system for process development, we have tested growth and production performance of CHO cells in 24DW plates and conventional shake flask cultures. Multiple studies were performed to assess well-to-well and plate-to-plate variability in 24DW plates. Additional studies were performed to determine the applicability of 24DW plates for cell culture medium and supplement screening in batch and fed batch processes. Cultures in 24DW plates exhibited similar kinetics in growth, viability and protein production to those cultured in shake flasks, suggesting that 24DW plates with Duetz sandwich-covers can be effectively used for high throughput cell culture screening.
Keywords: %CV, percent coefficient of variation; 24DW, 24 deep well; Batch; CD, chemically defined; CHO cells; CHO cells, Chinese Hamster Ovarian cells; Cell culture; Deep well plates; Duetz sandwich-cover system; Fed batch; VCD, viable cell density.
Figures

References
-
- Patel M.I., Tuckerman R., Dong Q. A Pitfall of the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-5(3-carboxymethonyphenol)-2-(4-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium (MTS) assay due to evaporation in wells on the edge of a 96 well plate. Biotechnol. Lett. 2005;27:805–808. - PubMed
-
- Zimmermann H.F., John G., Trauthwein T., Dingerdissen H., Huthmacher U.K. Rapid evaluation of oxygen and water permeation through microplate sealing tapes. Biotechnol. Prog. 2003;19:1061–1063. - PubMed
-
- Duetz W.A., Minas W., Kuhner M., Clerval R., Fjallman A.H.M., Witholt B. Miniaturized microbial growth systems in screening. Bioworld. 2001;2:8–10.
-
- Duetz W.A., Witholt B. Oxygen transfer by orbital shaking of square vessels and deepwell microtiter plates of various dimensions. Biochem. Eng. J. 2004;17:181–185.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
