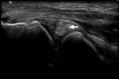
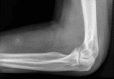
Spontaneous elbow hemarthrosis identified by point-of-care ultrasound
- PMID: 28435904
- PMCID: PMC5385507
- DOI: 10.15441/ceem.16.137
Spontaneous elbow hemarthrosis identified by point-of-care ultrasound
Abstract
Traumatic or spontaneous hemarthroses are an important cause of joint effusions, and can complicate innate or acquired coagulopathies. The elbow is an unusual location for a spontaneous hemarthrosis; we describe a previously unreported case of warfarin-induced spontaneous elbow hemarthrosis, diagnosed by point-of-care ultrasound. On the basis of clinical and ultrasound findings arthrocentesis was deferred, and the patient was successfully treated with warfarin reversal and conservative care. Physical examination is unreliable for the detection of a joint effusion, and misdiagnosis and can lead to unnecessary investigation or resource use. Point-of-care ultrasound allows accurate, prompt, direct visualization of a joint effusion, and non-invasive confirmation of a hemarthrosis. Ultrasound can facilitate accurate diagnosis and characterization of joint effusions to improve the care of patients with coagulopathy.
Keywords: Hemarthrosis; Joints; Ultrasonography; Warfarin.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Accelerating recovery from acute hemarthrosis in patients with hemophilia: the role of joint aspiration.Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2019 Apr;30(3):111-119. doi: 10.1097/MBC.0000000000000803. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2019. PMID: 30958454
-
The value of HEAD-US system in detecting subclinical abnormalities in joints of patients with hemophilia.Expert Rev Hematol. 2018 Mar;11(3):253-261. doi: 10.1080/17474086.2018.1435269. Epub 2018 Feb 15. Expert Rev Hematol. 2018. PMID: 29383965
-
Point-of-care musculoskeletal ultrasound is critical for the diagnosis of hemarthroses, inflammation and soft tissue abnormalities in adult patients with painful haemophilic arthropathy.Haemophilia. 2015 Jul;21(4):530-7. doi: 10.1111/hae.12637. Epub 2015 Jan 27. Haemophilia. 2015. PMID: 25623830
-
Hemophilic arthropathy of the elbow: prophylaxis, imaging, and the role of invasive management.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2015 Oct;24(10):1669-78. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2015.06.018. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2015. PMID: 26385390 Review.
-
[Spontaneous hemarthrosis in adolescents and adults, excluding hemophilia].Sem Hop. 1982 Nov 11;58(41):2367-73. Sem Hop. 1982. PMID: 6297020 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Management of Haemarthrosis in Patients On Oral Anticoagulants.Geriatr Orthop Surg Rehabil. 2022 May 11;13:21514593221076966. doi: 10.1177/21514593221076966. eCollection 2022. Geriatr Orthop Surg Rehabil. 2022. PMID: 35573907 Free PMC article.
-
Spontaneous atraumatic heparin-induced hemarthrosis in a patient treated for non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction.Radiol Case Rep. 2023 Feb 13;18(4):1596-1600. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2023.01.042. eCollection 2023 Apr. Radiol Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 36852288 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nawar EW, Niska RW, Xu J. National Hospital Ambulatory Medical Care Survey: 2005 emergency department summary. Adv Data. 2007;(386):1–32. - PubMed
-
- Ceponis A, Wong-Sefidan I, Glass CS, von Drygalski A. Rapid musculoskeletal ultrasound for painful episodes in adult haemophilia patients. Haemophilia. 2013;19:790–8. - PubMed
-
- Hauzeur JP, Mathy L, De Maertelaer V. Comparison between clinical evaluation and ultrasonography in detecting hydrarthrosis of the knee. J Rheumatol. 1999;26:2681–3. - PubMed
-
- Valley VT, Stahmer SA. Targeted musculoarticular sonography in the detection of joint effusions. Acad Emerg Med. 2001;8:361–7. - PubMed
-
- Dubrovsky AS, Kempinska A, Bank I, Mok E. Accuracy of ultrasonography for determining successful realignment of pediatric forearm fractures. Ann Emerg Med. 2015;65:260–5. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources