The C677T variant in MTHFR modulates associations between brain integrity, mood, and cognitive functioning in old age
- PMID: 28435933
- PMCID: PMC5395287
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpsc.2016.09.005
The C677T variant in MTHFR modulates associations between brain integrity, mood, and cognitive functioning in old age
Abstract
Introduction: The C677T functional variant in the methylene-tetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) gene leads to reduced enzymatic activity and elevated blood levels of homocysteine. Hyperhomocysteinemia has been linked with higher rates of cardiovascular diseases, cognitive decline, and late-life depression.
Methods and materials: Here, 3D magnetic resonance imaging data was analyzed from 738 individuals (age: 75.5 ± 6.8 years; 438 men/300 women) including 173 Alzheimer's patients, 359 subjects with mild cognitive impairment, and 206 healthy older adults, scanned as part of the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI).
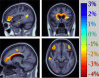
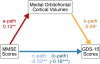
Results: We found that this variant associates with localized brain atrophy, after controlling for age, sex, and dementia status, in brain regions implicated in both intellectual and emotional functioning, notably the medial orbitofrontal cortices. The medial orbitofrontal cortex is involved in the cognitive modulation of emotional processes, and localized atrophy in this region was previously linked with both cognitive impairment and depressive symptoms. Here, we report that increased plasma homocysteine mediates the association between MTHFR genotype and lower medial orbitofrontal volumes, and that these volumes mediate the association between cognitive decline and depressed mood in this elderly cohort. We additionally show that vitamin B12 deficiency interacts with the C677T variant in the etiology of hyperhomocysteinemia.
Conclusion: This study sheds light on important relationships between vascular risk factors, age-related cognitive decline, and late-life depression, and represents a significant advance in our understanding of clinically relevant associations relating to MTHFR genotype.
Keywords: MRI; MTHFR; age-related cognitive decline; brain atrophy; homocysteine; late-life depression.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Common folate gene variant, MTHFR C677T, is associated with brain structure in two independent cohorts of people with mild cognitive impairment.Neuroimage Clin. 2012 Oct 4;1(1):179-87. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2012.09.012. eCollection 2012. Neuroimage Clin. 2012. PMID: 24179750 Free PMC article.
-
The C677T variant in MTHFR modulates associations between blood-based and cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers of neurodegeneration.Neuroreport. 2016 Aug 17;27(12):948-51. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000000636. Neuroreport. 2016. PMID: 27380243 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma folate, vitamin B(12), and total homocysteine and homozygosity for the C677T mutation of the 5,10-methylene tetrahydrofolate reductase gene in patients with Alzheimer's dementia. A case-control study.Gerontology. 2001 Nov-Dec;47(6):324-9. doi: 10.1159/000052822. Gerontology. 2001. PMID: 11721146
-
MTHFR gene polymorphism, homocysteine and cardiovascular disease.Public Health Nutr. 2001 Apr;4(2B):493-7. doi: 10.1079/phn2001159. Public Health Nutr. 2001. PMID: 11683544 Review.
-
Correlation between C677T MTHFR gene polymorphism, plasma homocysteine levels and the incidence of CAD.Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2001;1(5):353-61. doi: 10.2165/00129784-200101050-00005. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2001. PMID: 14728017 Review.
Cited by
-
Association of Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase C677T Gene Polymorphisms with Mild Cognitive Impairment Susceptibility: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Behav Neurol. 2021 Sep 18;2021:2962792. doi: 10.1155/2021/2962792. eCollection 2021. Behav Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34580600 Free PMC article.
-
The Influence of MTHFR Polymorphism on Gray Matter Volume in Patients With Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment.Front Neurosci. 2021 Nov 30;15:778123. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.778123. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34916904 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Unhealthy Lifestyle and Genetic Risk Factors With Mild Cognitive Impairment in Chinese Older Adults.JAMA Netw Open. 2023 Jul 3;6(7):e2324031. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.24031. JAMA Netw Open. 2023. PMID: 37462970 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Cocktail Approach for Treatment of Hyperhomocysteinemia in Alzheimer's Disease.Cell Med. 2018 Jan 25;10:2155179017722280. doi: 10.1177/2155179017722280. eCollection 2018. Cell Med. 2018. PMID: 32634177 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Behavioral and Psychological Symptoms of Dementia (BPSD): Clinical Characterization and Genetic Correlates in an Italian Alzheimer's Disease Cohort.J Pers Med. 2020 Aug 14;10(3):90. doi: 10.3390/jpm10030090. J Pers Med. 2020. PMID: 32823921 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cattaneo M. Hyperhomocysteinemia, atherosclerosis and thrombosis. Thrombosis and haemostasis. 1999;81:165–176. - PubMed
-
- Zhou J, Austin RC. Contributions of hyperhomocysteinemia to atherosclerosis: Causal relationship and potential mechanisms. Biofactors. 2009;35:120–129. - PubMed
-
- McIlroy SP, Dynan KB, Lawson JT, Patterson CC, Passmore AP. Moderately elevated plasma homocysteine, methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase genotype, and risk for stroke, vascular dementia, and Alzheimer disease in Northern Ireland. Stroke; a journal of cerebral circulation. 2002;33:2351–2356. - PubMed
-
- Budge MM, de Jager C, Hogervorst E, Smith AD, Oxford Project To Investigate M, Ageing Total plasma homocysteine, age, systolic blood pressure, and cognitive performance in older people. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 2002;50:2014–2018. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
