Whole genome sequence association and ancestry-informed polygenic profile of EEG alpha in a Native American population
- PMID: 28436151
- PMCID: PMC5435561
- DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.b.32533
Whole genome sequence association and ancestry-informed polygenic profile of EEG alpha in a Native American population
Abstract
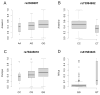
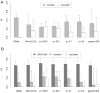
EEG alpha activity is the dominant oscillation in most adult humans, is highly heritable, and has been associated with a number of cognitive functions. Two EEG phenotypes, low- and high-voltage alpha (LVA & HVA), have been demonstrated to have high heritabilities. They have different prevalence depending on a population's ancestral origins. In the present study we assessed the influence of ancestry admixture on EEG alpha power, and conducted a whole genome sequencing association analysis and an ancestry-informed polygenic study on those phenotypes in a Native American (NA) population that has a high prevalence of LVA. Seven common variants, in LD with each other upstream from gene ASIC2, reached genome-wide significance (p = 2 × 10-8 ) having a positive association with alpha voltage. They had lower minor allele frequencies in the NAs than in a global population sample. Overall correlations between lower degrees of NA (higher degree European) ancestry and HVA, and higher degrees of NA and LVA were also found. Additionally a rare-variant gene-based study identified gene TIA1 being negatively associated with LVA. Approximately 3% of SNPs exhibited a 15-fold enrichment that explained nearly half of the total SNP-heritability for EEG alpha. These regions showed the most significant anti-correlations between NA ancestry and alpha voltage, and were enriched for genes and pathways mediating cognitive functions. Our findings suggested that these regions likely harbor causal variants for HVA, and lacking of such variants could explain the high prevalence of LVA in this NA population, possibly illuminating the ancestral origin and genetic basis for EEG alpha.
Keywords: admixture; gene based rare variant analysis; genome-wide association; heritability enrichment; low coverage sequencing.
© 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have any conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Adrian ED, Matthews BHC. The Berger rhythm: potential changes from the occipital lobes in man. Brain. 1934;57:355–385. - PubMed
-
- Anderson P, Kedersha N. Stress granules: the Tao of RNA triage. Trends in Biochemical Sciences. 2008;33:141–150. - PubMed
-
- Anokhin A, Steinlein O, Fischer C, Mao Y, Vogt P, Schalt E, Vogel F. A genetic study of the human low-voltage electroencephalogram. Hum Genet. 1992;90:99–112. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

