Identification of pro-inflammatory CD205+ macrophages in livers of hepatitis B virus transgenic mice and patients with chronic hepatitis B
- PMID: 28436459
- PMCID: PMC5402278
- DOI: 10.1038/srep46765
Identification of pro-inflammatory CD205+ macrophages in livers of hepatitis B virus transgenic mice and patients with chronic hepatitis B
Abstract
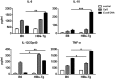
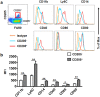
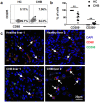
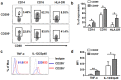
Hepatic macrophages play a central role in disease pathogenesis during hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. Our previous study found that CD205+ macrophages in the liver of hepatitis B surface antigen transgenic (HBs-Tg) mice increased significantly compared with those in wild-type mice, and these increased CD205+ macrophages were involved in CpG-oligodeoxynucleotide-induced liver injury in HBs-Tg mice. Here, we analysed the phenotype and function of CD205+ macrophages derived from the liver of HBs-Tg mice and patients with chronic hepatitis B (CHB). We found that HBs-Tg mice-derived hepatic macrophages produced larger amounts of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-6, IL-12, TNF-α, and of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 after stimulation with CpG-oligodeoxynucleotides or commensal bacteria DNA than B6 mice-derived hepatic macrophages. Furthermore, hepatic CD205+ macrophages from HBs-Tg mice showed an activated phenotype and expressed higher levels of inflammatory cytokine genes, chemokine genes, and phagocytosis-related genes than hepatic CD205- macrophages. In addition, CD205+ macrophages displayed an inflammatory phenotype and were increased in the liver of patients with CHB compared with those in healthy controls. Our data suggest that hepatic CD205+ macrophages are a unique pro-inflammatory subset observed during HBV infection. Thus, development of intervention targeting these cells is warranted for immunotherapy of HBV-induced liver diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
CD205-TLR9-IL-12 axis contributes to CpG-induced oversensitive liver injury in HBsAg transgenic mice by promoting the interaction of NKT cells with Kupffer cells.Cell Mol Immunol. 2017 Aug;14(8):675-684. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2015.111. Epub 2016 Apr 4. Cell Mol Immunol. 2017. PMID: 27041637 Free PMC article.
-
Viral Load Affects the Immune Response to HBV in Mice With Humanized Immune System and Liver.Gastroenterology. 2017 Dec;153(6):1647-1661.e9. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.08.034. Epub 2017 Aug 26. Gastroenterology. 2017. PMID: 28851562 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic CD206-positive macrophages express amphiregulin to promote the immunosuppressive activity of regulatory T cells in HBV infection.J Leukoc Biol. 2015 Dec;98(6):1071-80. doi: 10.1189/jlb.4A0415-152R. Epub 2015 Jul 27. J Leukoc Biol. 2015. PMID: 26216935
-
Hepatic macrophage niche: a bridge between HBV-mediated metabolic changes with intrahepatic inflammation.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 18;15:1414594. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1414594. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39091506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut microbiota in the innate immunity against hepatitis B virus - implication in age-dependent HBV clearance.Curr Opin Virol. 2021 Aug;49:194-202. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2021.06.006. Epub 2021 Jul 7. Curr Opin Virol. 2021. PMID: 34242953 Review.
Cited by
-
Insights into Hepatitis B Virus DNA Integration-55 Years after Virus Discovery.Innovation (Camb). 2020 Aug 5;1(2):100034. doi: 10.1016/j.xinn.2020.100034. eCollection 2020 Aug 28. Innovation (Camb). 2020. PMID: 34557710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resident Kupffer cells and neutrophils drive liver toxicity in cancer immunotherapy.Sci Immunol. 2021 Jul 2;6(61):eabi7083. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abi7083. Sci Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34215680 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatitis B Core Antigen Impairs the Polarization While Promoting the Production of Inflammatory Cytokines of M2 Macrophages via the TLR2 Pathway.Front Immunol. 2020 Mar 27;11:535. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00535. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32292408 Free PMC article.
-
HBeAg induces the expression of macrophage miR-155 to accelerate liver injury via promoting production of inflammatory cytokines.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018 Jul;75(14):2627-2641. doi: 10.1007/s00018-018-2753-8. Epub 2018 Jan 18. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 29349567 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of integrated hepatitis B virus DNA on oncogenesis and antiviral therapy.Biomark Res. 2024 Aug 15;12(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s40364-024-00611-y. Biomark Res. 2024. PMID: 39148134 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

