Genome-wide profiling of heritable and de novo STR variations
- PMID: 28436466
- PMCID: PMC5482724
- DOI: 10.1038/nmeth.4267
Genome-wide profiling of heritable and de novo STR variations
Abstract
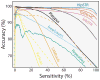
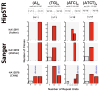
Short tandem repeats (STRs) are highly variable elements that play a pivotal role in multiple genetic diseases, population genetics applications, and forensic casework. However, it has proven problematic to genotype STRs from high-throughput sequencing data. Here, we describe HipSTR, a novel haplotype-based method for robustly genotyping and phasing STRs from Illumina sequencing data, and we report a genome-wide analysis and validation of de novo STR mutations. HipSTR is freely available at https://hipstr-tool.github.io/HipSTR.
Conflict of interest statement
Y.E. is a consultant for Arc Bio, a company interested in DNA forensics.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

