Redefining the identity of cardiac fibroblasts
- PMID: 28436487
- PMCID: PMC6329009
- DOI: 10.1038/nrcardio.2017.57
Redefining the identity of cardiac fibroblasts
Abstract
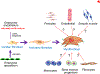
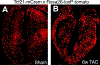
Cardiac fibroblasts deposit and maintain extracellular matrix during organogenesis and under physiological conditions. In the adult heart, activated cardiac fibroblasts also participate in the healing response after acute myocardial infarction and during chronic disease states characterized by augmented interstitial fibrosis and ventricular remodelling. However, delineation of the characteristics, plasticity, and origins of cardiac fibroblasts is an area of ongoing investigation and controversy. A set of genetic mouse models has been developed that specifically addresses the nature of these cells, in terms of both their origins and their response during cardiac disease and ventricular remodelling. As our understanding of cardiac fibroblasts becomes more defined and refined, so does the potential to develop new therapeutic strategies to control fibrosis and adverse ventricular remodelling.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Mozaffarian D et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2015 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 131, e29–322 (2015). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

