Disruption of tetR type regulator adeN by mobile genetic element confers elevated virulence in Acinetobacter baumannii
- PMID: 28436748
- PMCID: PMC5711439
- DOI: 10.1080/21505594.2017.1322240
Disruption of tetR type regulator adeN by mobile genetic element confers elevated virulence in Acinetobacter baumannii
Abstract
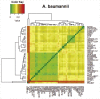
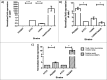
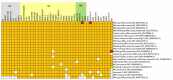
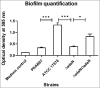
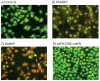
Acinetobacter baumannii is an important human pathogen and considered as a major threat due to its extreme drug resistance. In this study, the genome of a hyper-virulent MDR strain PKAB07 of A. baumannii isolated from an Indian patient was sequenced and analyzed to understand its mechanisms of virulence, resistance and evolution. Comparative genome analysis of PKAB07 revealed virulence and resistance related genes scattered throughout the genome, instead of being organized as an island, indicating the highly mosaic nature of the genome. Many intermittent horizontal gene transfer events, insertion sequence (IS) element insertions identified were augmenting resistance machinery and elevating the SNP densities in A. baumannii eventually aiding in their swift evolution. ISAba1, the most widely distributed insertion sequence in A. baumannii was found in multiple sites in PKAB07. Out of many ISAba1 insertions, we identified novel insertions in 9 different genes wherein insertional inactivation of adeN (tetR type regulator) was significant. To assess the significance of this disruption in A. baumannii, adeN mutant and complement strains were constructed in A. baumannii ATCC 17978 strain and studied. Biofilm levels were abrogated in the adeN knockout when compared with the wild type and complemented strain of adeN knockout. Virulence of the adeN knockout mutant strain was observed to be high, which was validated by in vitro experiments and Galleria mellonella infection model. The overexpression of adeJ, a major component of AdeIJK efflux pump observed in adeN knockout strain could be the possible reason for the elevated virulence in adeN mutant and PKB07 strain. Knocking out of adeN in ATCC strain led to increased resistance and virulence at par with the PKAB07. Disruption of tetR type regulator adeN by ISAba1 consequently has led to elevated virulence in this pathogen.
Keywords: Acinetobacter baumannii; SNPs; biofilm; efflux pumps; insertion sequence element; international clone II.
Figures

Comment in
-
The effect of ISAba1-mediated adeN gene disruption on Acinetobacter baumannii pathogenesis.Virulence. 2017 Oct 3;8(7):1088-1090. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2017.1339859. Epub 2017 Jun 9. Virulence. 2017. PMID: 28598246 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Dent LL, Marshall DR, Pratap S, Hulette RB. Multidrug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: a descriptive study in a city hospital. BMC Infect Dis 2010; 10:196; PMID:20609238; https://doi.org/ 10.1186/1471-2334-10-196 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Katsaragakis S, Markogiannakis H, Toutouzas KG, Drimousis P, Larentzakis A, Theodoraki EM, Theodorou D. Acinetobacter baumannii infections in a surgical intensive care unit: predictors of multi-drug resistance. World J Surg 2008; 32:1194-202; PMID:18408967; https://doi.org/ 10.1007/s00268-008-9571-3 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zarrilli R, Pournaras S, Giannouli M, Tsakris A. Global evolution of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii clonal lineages. Int J Antimicrob Agents 2013; 41:11-9; PMID:23127486; https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2012.09.008 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Adams MD, Chan ER, Molyneaux ND, Bonomo RA. Genome wide analysis of divergence of antibiotic resistance determinants in closely related isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2010; 54:3569-77; PMID:20530228; https://doi.org/ 10.1128/AAC.00057-10 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Corvec S, Caroff N, Espaze E, Giraudeau C, Drugeon H, Reynaud A. AmpC cephalosporinase hyperproduction in Acinetobacter baumannii clinical strains. J Antimicrob Chemother 2003; 52:629-35; PMID:12951337; https://doi.org/ 10.1093/jac/dkg407 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
