Vitamin A mediates conversion of monocyte-derived macrophages into tissue-resident macrophages during alternative activation
- PMID: 28436955
- PMCID: PMC5475284
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.3734
Vitamin A mediates conversion of monocyte-derived macrophages into tissue-resident macrophages during alternative activation
Abstract
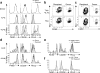
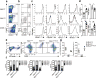
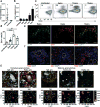
It remains unclear whether activated inflammatory macrophages can adopt features of tissue-resident macrophages, or what mechanisms might mediate such a phenotypic conversion. Here we show that vitamin A is required for the phenotypic conversion of interleukin 4 (IL-4)-activated monocyte-derived F4/80intCD206+PD-L2+MHCII+ macrophages into macrophages with a tissue-resident F4/80hiCD206-PD-L2-MHCII-UCP1+ phenotype in the peritoneal cavity of mice and during the formation of liver granulomas in mice infected with Schistosoma mansoni. The phenotypic conversion of F4/80intCD206+ macrophages into F4/80hiCD206- macrophages was associated with almost complete remodeling of the chromatin landscape, as well as alteration of the transcriptional profiles. Vitamin A-deficient mice infected with S. mansoni had disrupted liver granuloma architecture and increased mortality, which indicates that failure to convert macrophages from the F4/80intCD206+ phenotype to F4/80hiCD206- may lead to dysregulated inflammation during helminth infection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


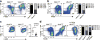


Comment in
-
Alternative monocytes settle in for the long term.Nat Immunol. 2017 May 18;18(6):599-600. doi: 10.1038/ni.3749. Nat Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28518159 No abstract available.
-
Macrophage's little helper: vitamin A directs alternatively activated monocyte-derived macrophages to tissue-resident macrophages.Cell Mol Immunol. 2017 Oct;14(10):805-808. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2017.58. Epub 2017 Jul 10. Cell Mol Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28690329 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

