Drainage Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy for Malignant Bowel Obstruction in Gastrointestinal Cancers: Prognosis and Implications for Timing of Palliative Intervention
- PMID: 28437204
- PMCID: PMC8349727
- DOI: 10.1089/jpm.2016.0465
Drainage Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy for Malignant Bowel Obstruction in Gastrointestinal Cancers: Prognosis and Implications for Timing of Palliative Intervention
Abstract
Background: Malignant bowel obstruction (MBO) is a frequent complication in patients with advanced solid tumors. Palliative relief may be achieved by the use of a drainage percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (dPEG) tube, although optimal timing of placement remains unknown.
Objectives: To determine median survival after diagnosis of MBO and dPEG placement, factors associated with worse survival in MBO, factors associated with receipt of dPEG, and association of timing of dPEG placement on survival.
Methods: This observational retrospective cohort study examined 439 patients with MBO on a gastrointestinal medical oncology inpatient service. Patients were characterized by age, gender, race, primary cancer type, length of stay, readmission, complications (aspiration pneumonia or bowel perforation), and receipt of dPEG. Select factors were analyzed to examine overall survival (OS) and dPEG placement.
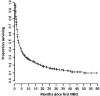
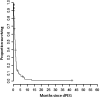
Results: Median survival from diagnosis of first MBO was 2.5 months. Median survival after dPEG placement was 37 days. In univariate analysis, dPEG placement, complications, longer length of stay, and readmissions were significantly associated with worse OS. Receipt of dPEG was significantly associated with younger age, longer length of stay at first admission, and shorter interval to readmission. In patients who received dPEG, longer interval from MBO diagnosis to dPEG placement did not affect OS.
Conclusion: We found that prognosis following diagnosis of MBO in patients with gastrointestinal malignancies remains poor. Our data suggest that timing of dPEG placement in MBO does not affect OS and, therefore, earlier intervention with this procedure may allow earlier and prolonged palliative relief.
Keywords: drainage percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy; gastrointestinal malignancy; malignant bowel obstruction.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Illness Understanding, Prognostic Awareness, and End-of-Life Care in Patients With GI Cancer and Malignant Bowel Obstruction With Drainage Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy.JCO Oncol Pract. 2021 Feb;17(2):e186-e193. doi: 10.1200/OP.20.00035. Epub 2020 Aug 6. JCO Oncol Pract. 2021. PMID: 32758086 Free PMC article.
-
Decompressive percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in advanced cancer patients with small-bowel obstruction is feasible and effective: a large prospective study.Support Care Cancer. 2016 Jul;24(7):2877-82. doi: 10.1007/s00520-016-3102-9. Epub 2016 Feb 2. Support Care Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26838026
-
Outcome of palliative operations for malignant bowel obstruction in patients with peritoneal carcinomatosis from nongynecological cancer.Ann Surg Oncol. 2001 Sep;8(8):632-7. doi: 10.1007/s10434-001-0632-1. Ann Surg Oncol. 2001. PMID: 11569777
-
Safety and Efficacy of Venting Gastrostomy in Malignant Bowel Obstruction: A Systematic Review.J Palliat Care. 2020 Apr;35(2):93-102. doi: 10.1177/0825859719864915. Epub 2019 Aug 25. J Palliat Care. 2020. PMID: 31448682
-
Decompressive percutaneous gastrostomy tube use in gynecologic malignancies.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2006 Mar;7(2):111-20. doi: 10.1007/s11864-006-0046-1. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2006. PMID: 16455022 Review.
Cited by
-
An overview of percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy tube placement in the intensive care unit.J Thorac Dis. 2021 Aug;13(8):5277-5296. doi: 10.21037/jtd-19-3728. J Thorac Dis. 2021. PMID: 34527366 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Illness Understanding, Prognostic Awareness, and End-of-Life Care in Patients With GI Cancer and Malignant Bowel Obstruction With Drainage Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy.JCO Oncol Pract. 2021 Feb;17(2):e186-e193. doi: 10.1200/OP.20.00035. Epub 2020 Aug 6. JCO Oncol Pract. 2021. PMID: 32758086 Free PMC article.
-
The Chicago Consensus on Peritoneal Surface Malignancies: Palliative Care Considerations.Ann Surg Oncol. 2020 Jun;27(6):1798-1804. doi: 10.1245/s10434-020-08323-x. Epub 2020 Apr 13. Ann Surg Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32285272
-
[Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in geriatrics : Indications, technique and complications].Z Gerontol Geriatr. 2018 Feb;51(2):237-245. doi: 10.1007/s00391-017-1363-7. Epub 2018 Jan 18. Z Gerontol Geriatr. 2018. PMID: 29349584 German.
-
MASCC multidisciplinary evidence-based recommendations for the management of malignant bowel obstruction in advanced cancer.Support Care Cancer. 2022 Jun;30(6):4711-4728. doi: 10.1007/s00520-022-06889-8. Epub 2022 Mar 10. Support Care Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35274188 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ripamonti C, Bruera E: Palliative management of malignant bowel obstruction. Int J Gynecol Cancer 2002;12:135–143 - PubMed
-
- Helyer L, Easson AM: Surgical approaches to malignant bowel obstruction. J Support Oncol 2008;6:105–113 - PubMed
-
- Chakraborty A, Selby D, Gardiner K, et al. : Malignant bowel obstruction: Natural history of a heterogeneous patient population followed prospectively over two years. J Pain Symptom Manage 2011;41:412–420 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

