ESPRIT-Forest: Parallel clustering of massive amplicon sequence data in subquadratic time
- PMID: 28437450
- PMCID: PMC5421816
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005518
ESPRIT-Forest: Parallel clustering of massive amplicon sequence data in subquadratic time
Abstract
The rapid development of sequencing technology has led to an explosive accumulation of genomic sequence data. Clustering is often the first step to perform in sequence analysis, and hierarchical clustering is one of the most commonly used approaches for this purpose. However, it is currently computationally expensive to perform hierarchical clustering of extremely large sequence datasets due to its quadratic time and space complexities. In this paper we developed a new algorithm called ESPRIT-Forest for parallel hierarchical clustering of sequences. The algorithm achieves subquadratic time and space complexity and maintains a high clustering accuracy comparable to the standard method. The basic idea is to organize sequences into a pseudo-metric based partitioning tree for sub-linear time searching of nearest neighbors, and then use a new multiple-pair merging criterion to construct clusters in parallel using multiple threads. The new algorithm was tested on the human microbiome project (HMP) dataset, currently one of the largest published microbial 16S rRNA sequence dataset. Our experiment demonstrated that with the power of parallel computing it is now compu- tationally feasible to perform hierarchical clustering analysis of tens of millions of sequences. The software is available at http://www.acsu.buffalo.edu/∼yijunsun/lab/ESPRIT-Forest.html.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
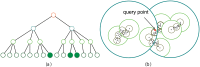
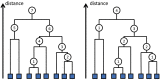
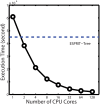
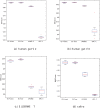
Similar articles
-
A parallel computational framework for ultra-large-scale sequence clustering analysis.Bioinformatics. 2019 Feb 1;35(3):380-388. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty617. Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 30010718 Free PMC article.
-
ESPRIT-Tree: hierarchical clustering analysis of millions of 16S rRNA pyrosequences in quasilinear computational time.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Aug;39(14):e95. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr349. Epub 2011 May 19. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 21596775 Free PMC article.
-
CLUSTOM-CLOUD: In-Memory Data Grid-Based Software for Clustering 16S rRNA Sequence Data in the Cloud Environment.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 8;11(3):e0151064. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151064. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26954507 Free PMC article.
-
CLUSTOM: a novel method for clustering 16S rRNA next generation sequences by overlap minimization.PLoS One. 2013 May 1;8(5):e62623. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062623. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23650520 Free PMC article.
-
MtHc: a motif-based hierarchical method for clustering massive 16S rRNA sequences into OTUs.Mol Biosyst. 2015 Jul;11(7):1907-13. doi: 10.1039/c5mb00089k. Mol Biosyst. 2015. PMID: 25912934
Cited by
-
MicroPheno: predicting environments and host phenotypes from 16S rRNA gene sequencing using a k-mer based representation of shallow sub-samples.Bioinformatics. 2018 Jul 1;34(13):i32-i42. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty296. Bioinformatics. 2018. PMID: 29950008 Free PMC article.
-
DMSC: A Dynamic Multi-Seeds Method for Clustering 16S rRNA Sequences Into OTUs.Front Microbiol. 2019 Mar 12;10:428. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00428. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30915052 Free PMC article.
-
Accurately clustering biological sequences in linear time by relatedness sorting.Nat Commun. 2024 Apr 8;15(1):3047. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-47371-9. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38589369 Free PMC article.
-
Alignment-free comparison of metagenomics sequences via approximate string matching.Bioinform Adv. 2022 Oct 21;2(1):vbac077. doi: 10.1093/bioadv/vbac077. eCollection 2022. Bioinform Adv. 2022. PMID: 36388153 Free PMC article.
-
A parallel computational framework for ultra-large-scale sequence clustering analysis.Bioinformatics. 2019 Feb 1;35(3):380-388. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty617. Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 30010718 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

