Development and effectiveness of a mobile phone application conducting health behavioral intervention among men who have sex with men, a randomized controlled trial: study protocol
- PMID: 28438144
- PMCID: PMC5402667
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-017-4235-6
Development and effectiveness of a mobile phone application conducting health behavioral intervention among men who have sex with men, a randomized controlled trial: study protocol
Abstract
Background: Behavioral intervention is a key approach to HIV prevention among men who have sex with men (MSM). Widespread use of mobile phones provide us with novel opportunities to decrease HIV infection and transmission of MSM. The objective of the study was to design and develop a mobile phone application (app) aims to conduct behavioral intervention to MSM and to evaluate the efficacy of the app-based intervention compared to usual care, to analyze cost-effectiveness and mechanism of the intervention.
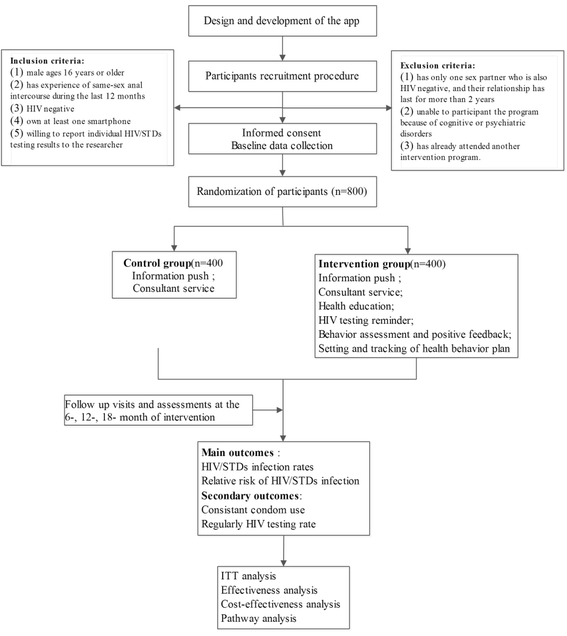
Methods: This study involves 2 phases, phase 1 use qualitative method and phase 2 is a randomized controlled trial lasting for 18 months, they will be conducted in Chagnsha, Hunan Province, China. Phase 1 is to design and develop the app, procedures including retrieval of domestic apps related to prevention and treatment about HIV and sexually transmitted diseases (HIV/STDs), personal interviews with MSM about preferences and functional needs of the HIV prevention app, multidisciplinary experts focused group discussions of the app, software engineers' development and users test of the app will be performed. In phase 2, we will recruit 800 MSM by cooperating with the local center of disease control and prevention and nongovernmental organizations, and divide them into intervention and control group evenly. Intervention group participants will receive app-based HIV prevention. Control group participants will be provided with usual care including HIV/STDs knowledge brochure and free voluntary counseling services. Data will be collected at baseline, 6, 12 and 18 months since subject's participation. Effectiveness of the intervention includes HIV/STDs infection rates, adherence to regularly HIV testing, sexual risk behavior, consistent condom use and relative risk of HIV infection. Cost-effectiveness will be analyzed by decision-analytic modeling, and mechanism analysis of this app-based intervention will be performed by path analysis.
Discussion: This will be the first study of its kind in China to develop an app and implement app-based HIV prevention intervention among MSM. It is of great potential to determine whether app-based intervention is a cost-effective way to decrease HIV infection among MSM and explore intervention mechanism with an accurate method.
Trial registration: Chinese Clinical Trial Register ( ChiCTR-IOR-15006724 ). Registered 10 July 2015.
Keywords: Behavioral intervention; Condom use; HIV testing; HIV/STDs; Men who have sex with men; Mobile phone application.
Similar articles
-
Protect MSM from HIV and other sexually transmitted diseases by providing mobile health services of partner notification: protocol for a pragmatic stepped wedge cluster randomized controlled trial.BMC Public Health. 2020 Jul 14;20(1):1107. doi: 10.1186/s12889-020-09162-x. BMC Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32664934 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The safe use of dating applications among men who have sex with men: a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial to evaluate an interactive web-based intervention to reduce risky sexual behaviours.BMC Public Health. 2020 May 27;20(1):795. doi: 10.1186/s12889-020-08914-z. BMC Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32460748 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between the use of gay mobile phone applications and HIV infection among men who have sex with men in Ningbo, China: a cross-sectional study.Int J STD AIDS. 2018 Apr;29(5):491-497. doi: 10.1177/0956462417738468. Epub 2017 Nov 3. Int J STD AIDS. 2018. PMID: 29099328
-
Mobile phone applications for the care and prevention of HIV and other sexually transmitted diseases: a review.J Med Internet Res. 2013 Jan 4;15(1):e1. doi: 10.2196/jmir.2301. J Med Internet Res. 2013. PMID: 23291245 Free PMC article. Review.
-
STIs and HIV among men having sex with men in China: a ticking time bomb?AIDS Educ Prev. 2009 Oct;21(5):430-46. doi: 10.1521/aeap.2009.21.5.430. AIDS Educ Prev. 2009. PMID: 19842827 Review.
Cited by
-
Use of Behavior Change Techniques in Digital HIV Prevention Programs for Adolescents and Young People: Systematic Review.JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2025 Apr 28;11:e59519. doi: 10.2196/59519. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2025. PMID: 40293783 Free PMC article.
-
Addressing Health Inequities in Digital Clinical Trials: A Review of Challenges and Solutions From the Field of HIV Research.Epidemiol Rev. 2022 Dec 21;44(1):87-109. doi: 10.1093/epirev/mxac008. Epidemiol Rev. 2022. PMID: 36124659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence and associated factors of HIV self-testing among men who have sex with men in Ningbo, China: a cross-sectional study.AIDS Res Ther. 2021 Apr 20;18(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s12981-021-00339-x. AIDS Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 33879191 Free PMC article.
-
The Characteristics and Quality of Mobile Phone Apps Targeted at Men Who Have Sex With Men in China: A Window of Opportunity for Health Information Dissemination?JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2019 Mar 27;7(3):e12573. doi: 10.2196/12573. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2019. PMID: 30916658 Free PMC article.
-
Update on human papillomavirus - Part II: complementary diagnosis, treatment and prophylaxis.An Bras Dermatol. 2021 Mar-Apr;96(2):125-138. doi: 10.1016/j.abd.2020.11.005. Epub 2021 Feb 16. An Bras Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 33637397 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC HIV and AIDS--United States, 1981-2000 [J] MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2001;50(21):430. - PubMed
-
- Zheng X. A report on AIDS surveillance report from 1985 to 1988 in China [J] Chin J Epidemiol. 1989;10:65–67. - PubMed
-
- Wu ZY. Chinese response on the spread of HIV/AIDS among MSM [C]. National communication about HIV prevention and control among MSM, tenth anniversary of FRIENDS program and Bailey-Martin prize award ceremony, Beijing, 2008.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical