Anti-depressant and anxiolytic potential of Acacia hydaspica R. Parker aerial parts extract: Modulation of brain antioxidant enzyme status
- PMID: 28438149
- PMCID: PMC5402641
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-017-1671-x
Anti-depressant and anxiolytic potential of Acacia hydaspica R. Parker aerial parts extract: Modulation of brain antioxidant enzyme status
Abstract
Background: Oxidative stress may link to psychiatric disorders, and is being regarded as a plausible mechanism that can affect the regulation of these illnesses. The present study was undertaken to investigate the antidepressant and anxiolytic potential of A. hydaspica R. parkers. Brain oxidative stress enzyme levels were analyzed to correlate depression and stress with brain antioxidant status.
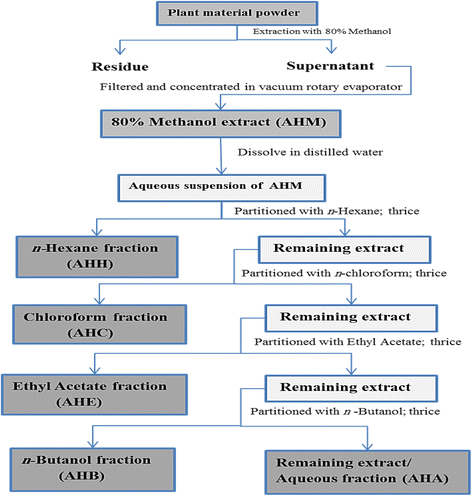
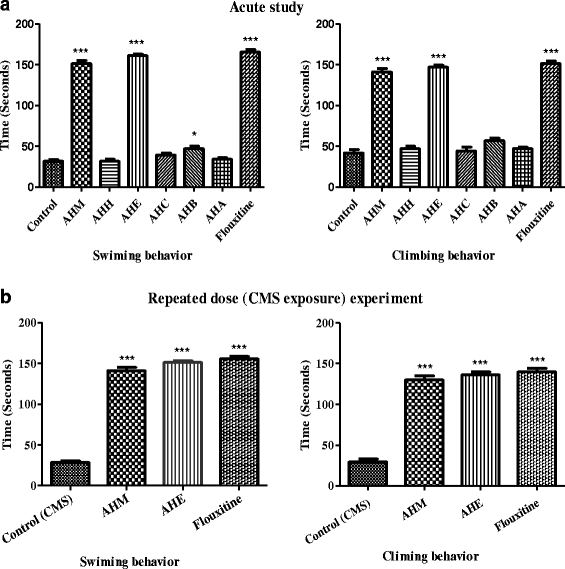
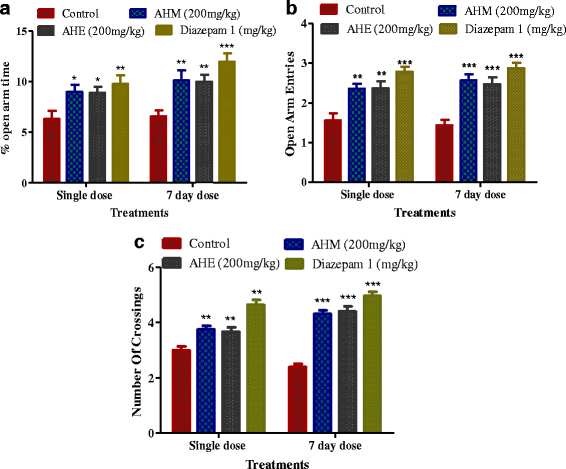
Methods: Antidepressant and anxiolytic effect of methanol extract of A. hydaspica and its derived soluble fractions [n-hexane (AHH), ethyl-acetate (AHE), chloroform (AHC), n-butanol (AHB) and remaining aqueous fraction (AHA)] was investigated by using three behavioral models; the Forced swimming test, Tail suspension test and Elevated plus-maze test (EPM). Chronic unpredictable mild stress (CMS) was employed to induce stress in rats. AHM and AHE (200 mg/kg, p.o), fluoxetine (5 mg/kg, i.p) and diazepam (DZM) (1 mg/kg, p.o) were administered during the 7 day stress exposure period, and rats were assessed for antidepressant and anxiolytic behavioral despair paradigms. Antioxidant enzymes and oxidative stress markers were measured in brain tissue of depressed rats. Phytochemical analysis was done by GCMS experimentation.
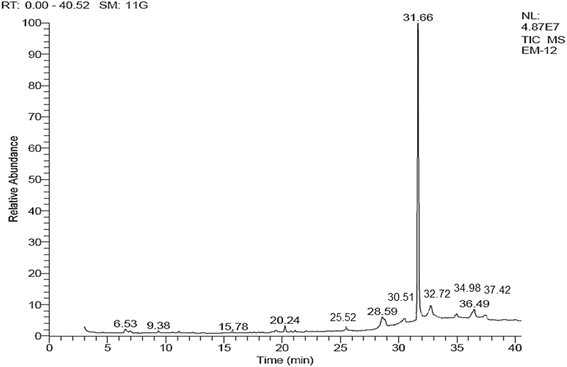
Results: AHM and AHE (acute dose) significantly (p < 0.0001) reduced the immobility time and ameliorated climbing behavior as compared to the control in FST and TST, and similar to fluoxetine. AHM and AHE showed significant (p < 0.0001) anxiolytic potential in EPM, and comparable to DZM (1 mg/kg b.w., i.p). Significant decrease in antioxidant enzyme levels and increase in MDA, H2O2 and NO level were observed in stressed rats. AHM and AHE (for 7 days/CMS) significantly improved behavior in FST, TST and EPMT. Treatment also improved antioxidant enzyme level and controlled the oxidative stress markers in brain tissues. GCMS analysis indicated the presence of 10 different chemical constituents in A. hydaspica.
Conclusion: The present study revealed that A. hydaspica exerts an antidepressant and anxiolytic effect by improving brain antioxidant status. The observed activities might be due to the presence of diverse phytochemicals.
Keywords: Brain antioxidants; Depression; Force swimming test; GCMS; Immobility time; Phytochemicals.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluating the protective potency of Acacia hydaspica R. Parker on histological and biochemical changes induced by Cisplatin in the cardiac tissue of rats.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019 Jul 23;19(1):182. doi: 10.1186/s12906-019-2575-8. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019. PMID: 31337380 Free PMC article.
-
Modulatory influence of Acacia hydaspica R. Parker ethyl acetate extract against cisplatin inveigled hepatic injury and dyslipidemia in rats.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Jun 12;17(1):307. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-1824-y. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 28606074 Free PMC article.
-
Acacia hydaspica R. Parker ameliorates cisplatin induced oxidative stress, DNA damage and morphological alterations in rat pulmonary tissue.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018 Feb 2;18(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s12906-018-2113-0. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018. PMID: 29394892 Free PMC article.
-
The neurodegenerative hypothesis of depression and the influence of antidepressant medications.Eur J Pharmacol. 2024 Nov 15;983:176967. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.176967. Epub 2024 Sep 1. Eur J Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39222740 Review.
-
Exploring the Therapeutic Potential of Terpenoids for Depression and Anxiety.Chem Biodivers. 2024 Oct;21(10):e202400788. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202400788. Epub 2024 Aug 27. Chem Biodivers. 2024. PMID: 38934531 Review.
Cited by
-
Acacia hydaspica R. Parker ethyl-acetate extract abrogates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by targeting ROS and inflammatory cytokines.Sci Rep. 2021 Aug 26;11(1):17248. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-96509-y. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34446789 Free PMC article.
-
Mustard Leaf Extract Suppresses Psychological Stress in Chronic Restraint Stress-Subjected Mice by Regulation of Stress Hormone, Neurotransmitters, and Apoptosis.Nutrients. 2020 Nov 26;12(12):3640. doi: 10.3390/nu12123640. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 33256231 Free PMC article.
-
Bioassay-guided isolation and characterization of lead antimicrobial compounds from Acacia hydaspica plant extract.AMB Express. 2022 Dec 15;12(1):156. doi: 10.1186/s13568-022-01501-y. AMB Express. 2022. PMID: 36520322 Free PMC article.
-
Reversal of cisplatin triggered neurotoxicity by Acacia hydaspica ethyl acetate fraction via regulating brain acetylcholinesterase activity, DNA damage, and pro-inflammatory cytokines in the rodent model.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022 Jul 5;22(1):179. doi: 10.1186/s12906-022-03657-3. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022. PMID: 35790919 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Inflammatory, Antioxidant, and Neuroprotective Effects of Polyphenols-Polyphenols as an Element of Diet Therapy in Depressive Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 23;24(3):2258. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032258. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768580 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Organization WH . 1999 World Health Organization-International Society of Hypertension guidelines for the management of hypertension: WHO. 1999.
-
- McKinney W, Moran E, Kraemer G. Separation in nonhuman primates as a model for human depression: neurobiological implications, Neurobiology of mood disorders (pp 393ą406). Baltimore, Williams and Wilkins; 1984.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

