Recent advances of highly selective CDK4/6 inhibitors in breast cancer
- PMID: 28438180
- PMCID: PMC5404666
- DOI: 10.1186/s13045-017-0467-2
Recent advances of highly selective CDK4/6 inhibitors in breast cancer
Abstract
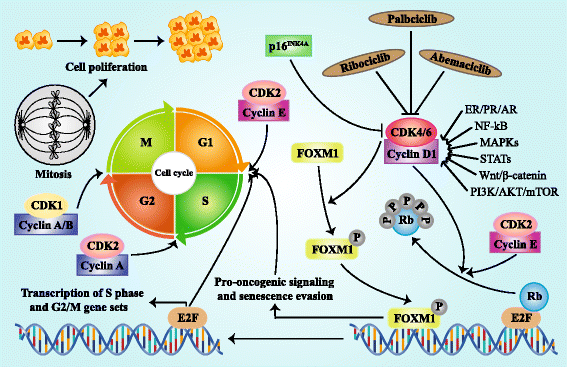
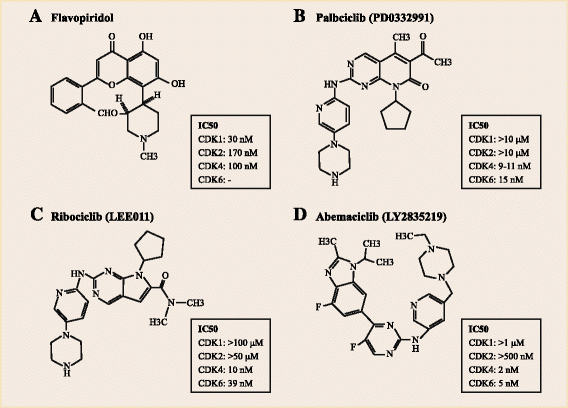
Uncontrolled cell division is the hallmark of cancers. Full understanding of cell cycle regulation would contribute to promising cancer therapies. In particular, cyclin-dependent kinases 4/6 (CDK4/6), which are pivotal drivers of cell proliferation by combination with cyclin D, draw more and more attention. Subsequently, extensive studies were carried out to explore drugs inhibiting CDK4/6 and assess the efficacy and safety of these drugs in cancer, especially breast cancer. Due to the insuperable adverse events and the less activity observed in vivo, the drug development of the initial pan-CDK inhibitor flavopiridol was consequently discontinued, and then highly specific inhibitors were extensively researched and developed, including palbociclib (PD0332991), ribociclib (LEE011), and abemaciclib (LY2835219). Food and Drug Administration has approved palbociclib and ribociclib for the treatment of hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative advanced or metastatic breast cancer, and recent clinical trial data suggest that palbociclib significantly improved clinical outcome when combined with letrozole or fulvestrant. Besides, the favorable effects of abemaciclib on prolonging survival of breast cancer patients have also been observed in clinical trials both for single-agent and combination strategy. In this review, we outline the preclinical and clinical advancement of these three orally bioavailable and highly selective CDK4/6 inhibitors in breast cancer.
Keywords: Abemaciclib; Breast cancer; CDK4/6 inhibitors; Palbociclib; Ribociclib; Safety; Treatment resistance.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors in breast cancer: palbociclib, ribociclib, and abemaciclib.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2017 Nov;166(1):41-54. doi: 10.1007/s10549-017-4385-3. Epub 2017 Jul 24. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2017. PMID: 28741274 Review.
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors for the management of advanced or metastatic breast cancer in women.Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2019 Aug 1;76(16):1183-1202. doi: 10.1093/ajhp/zxz121. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2019. PMID: 31369120 Review.
-
[Cell cycle inhibitors in endocrine receptor positive breast cancer].Bull Cancer. 2017 Feb;104(2):114-122. doi: 10.1016/j.bulcan.2016.12.005. Epub 2017 Jan 23. Bull Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28126188 French.
-
Comparison of treatment-related adverse events of different Cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors in metastatic breast cancer: A network meta-analysis.Cancer Treat Rev. 2020 Nov;90:102086. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2020.102086. Epub 2020 Aug 17. Cancer Treat Rev. 2020. PMID: 32861975
-
Clinical Management of Potential Toxicities and Drug Interactions Related to Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4/6 Inhibitors in Breast Cancer: Practical Considerations and Recommendations.Oncologist. 2017 Sep;22(9):1039-1048. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2017-0142. Epub 2017 Jul 13. Oncologist. 2017. PMID: 28706010 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fadraciclib (CYC065), a novel CDK inhibitor, targets key pro-survival and oncogenic pathways in cancer.PLoS One. 2020 Jul 9;15(7):e0234103. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0234103. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32645016 Free PMC article.
-
C4orf19 inhibits colorectal cancer cell proliferation by competitively binding to Keap1 with TRIM25 via the USP17/Elk-1/CDK6 axis.Oncogene. 2023 Apr;42(17):1333-1346. doi: 10.1038/s41388-023-02656-z. Epub 2023 Mar 7. Oncogene. 2023. PMID: 36882524
-
Microneedle Patch Delivery of PROTACs for Anti-Cancer Therapy.ACS Nano. 2023 Jun 27;17(12):11855-11868. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.3c03166. Epub 2023 Jun 9. ACS Nano. 2023. PMID: 37294705 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of the CDK4/6-Cyclin D-Rb Pathway by Ribociclib Augments Chemotherapy and Immunotherapy in Renal Cell Carcinoma.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Jun 11;2020:9525207. doi: 10.1155/2020/9525207. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32626773 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Cyclin-Dependent Kinases 4 and 6 Inhibitors in HR+/HER2- Advanced Breast Cancer.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 Jun 4;12:4241-4250. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S254365. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. PMID: 32581595 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

