Forced fluid removal versus usual care in intensive care patients with high-risk acute kidney injury and severe fluid overload (FFAKI): study protocol for a randomised controlled pilot trial
- PMID: 28438182
- PMCID: PMC5402636
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-017-1935-2
Forced fluid removal versus usual care in intensive care patients with high-risk acute kidney injury and severe fluid overload (FFAKI): study protocol for a randomised controlled pilot trial
Abstract
Background: Intravenous administration of fluids is an essential part of critical care. While some fluid administration is likely beneficial, there is increasing observational evidence that the development of fluid overload is associated with increased mortality. There are no randomised trials to confirm this association in patients with acute kidney injury. We aim to perform a pilot trial to test the feasibility of forced fluid removal compared to standard care in patients with acute kidney injury and severe fluid overload, the FFAKI trial.
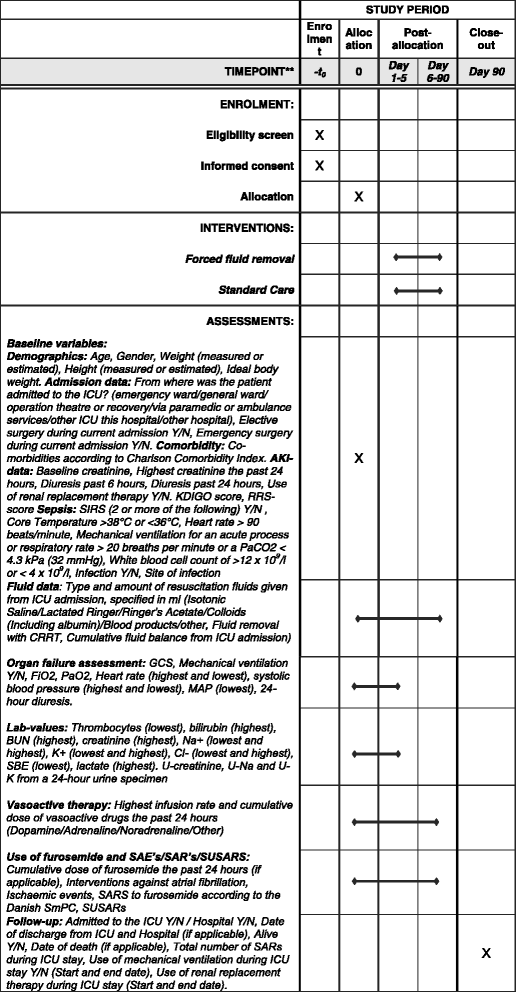
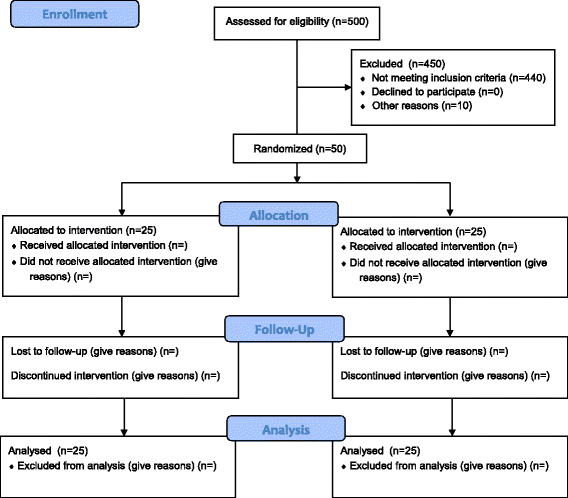
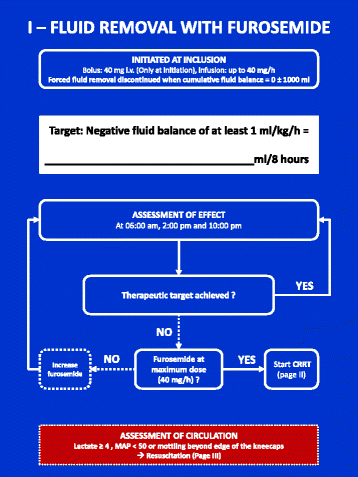
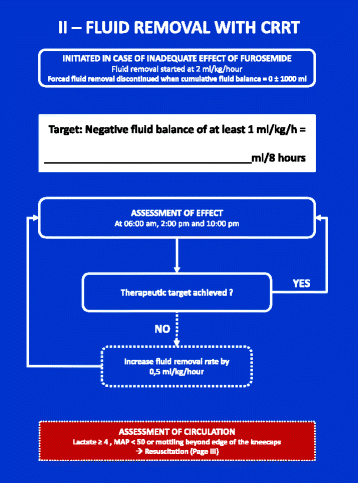
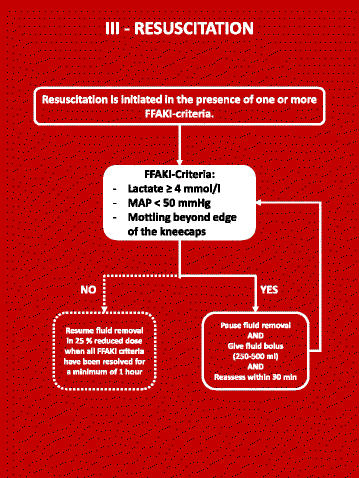
Methods: Then FFAKI trial is a pilot, multicentre, randomised clinical trial recruiting adult intensive care patients with acute kidney injury and fluid overload, defined as more than 10% of ideal bodyweight. Patients are randomised with concealed allocation to either standard care or forced fluid removal with a therapeutic target of negative net fluid balance ≥1 mL/kg/h. The safety of fluid removal is continually evaluated according to predefined criteria of hypoperfusion: lactate ≥4 mmol/L, mean arterial pressure <50 mmHg or mottling beyond the edge of the kneecaps. If patients fulfil one of these criteria, fluid removal is suspended until hypoperfusion has resolved. The primary outcome measure is fluid balance at 5 days after randomisation and secondary outcomes include mean daily fluid balance, fluid balance at discharge from the intensive care unit, time to neutral fluid balance, number of serious adverse reactions and number of protocol violations. All patients are followed for 90 days.
Discussion: The FFAKI trial started in October 2015 and, when completed, will provide data to evaluate whether a large trial of forced fluid removal in critically ill patients is feasible. Our primary outcome will show if the experimental intervention leads to a clinically relevant difference in fluid balance, which could prove beneficial in intensive care patients with acute kidney injury.
Trial registration: EudraCT, identifier: 2015-001701-13. Registered on 19 September 2015; ClinicalTrials.gov, identifier: NCT02458157 . Registered on 21 May 2015; Danish Ethics Committee, identifier: H-15009589H. Registered on 22 September 2015; Danish Health and Medicines Authority, identifier: 2015070013. Registered on 11 August 2015.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Feasibility trial; Fluid; Fluid overload; Intensive care; Randomised trial.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

