Comparison of the efficacy between conventional moxibustion and smoke-free moxibustion on knee osteoarthritis: study protocol of a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 28438185
- PMCID: PMC5402673
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-017-1846-2
Comparison of the efficacy between conventional moxibustion and smoke-free moxibustion on knee osteoarthritis: study protocol of a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Conventional moxibustion is a representative non-drug intervention in traditional Chinese medicine, and it has been reported to produce encouraging results and benefits in relieving symptoms and improving the quality of life for patients with knee osteoarthritis (KOA) in previous clinical trials and systematic reviews. Given that increasing concerns on the safety of generated smoke from conventional moxibustion have received much attention, smoke-free moxibustion is regarded as a potential alternative. However, whether smoke-free moxibustion would display a similar efficacy to that of conventional moxibustion still remains unclear. Therefore, this randomized controlled trial attempts to investigate the difference of efficacy between conventional moxibustion and smoke-free moxibustion in patients with KOA.
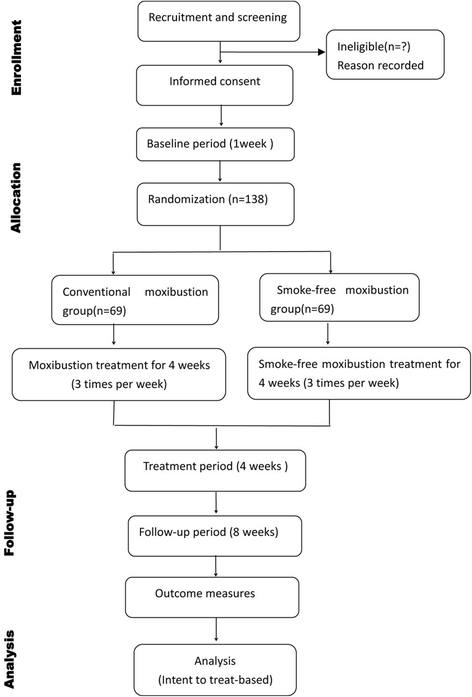
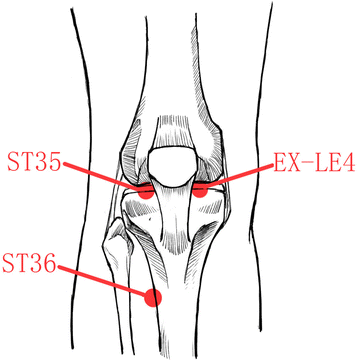
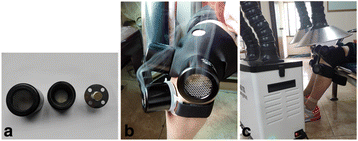
Methods/design: This is a multicenter, randomized, single-blinded, parallel-group clinical trial. A total of 138 eligible participants with KOA will be randomly allocated to two groups (conventional moxibustion group and smoke-free moxibustion group) in seven hospitals in China. Participants will receive 12 sessions of moxibustion treatment at three acupoints (EX-LE4, ST35, and ST36) over a period of 4 weeks (3 sessions per week). A smoke-removing device is placed at the top of the moxibustion device for the smoke-free moxibustion group (n = 69), while the conventional moxibustion group (n = 69) is treated with traditional moxibustion. The primary outcome measure will be the change of the global scale of the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) from the baseline to 4 weeks. Secondary outcomes include the visual analog scale VASand Patient Global Assessment scores. Follow-up measurements will be performed on the 8th and 12th weeks after random allocation.
Discussion: This study will contribute to providing a solid foundation for the selection of moxibustion in clinical application as well as future research in moxibustion therapy.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT02772055 . Registered on 12 May 2016.
Keywords: Knee osteoarthritis; Moxa smoke; Moxibustion; Protocol; Randomized controlled trial.
Figures
References
-
- Osteoarthritis: care and management in adults [clinical guideline CG177]: methods, evidence and recommendations. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. http://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/CG177. Accessed Feb 2014.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

