Predicting liver SBRT eligibility and plan quality for VMAT and 4π plans
- PMID: 28438215
- PMCID: PMC5404690
- DOI: 10.1186/s13014-017-0806-z
Predicting liver SBRT eligibility and plan quality for VMAT and 4π plans
Abstract
Background: It is useful to predict planned dosimetry and determine the eligibility of a liver cancer patient for SBRT treatment using knowledge based planning (KBP). We compare the predictive accuracy using the overlap volume histogram (OVH) and statistical voxel dose learning (SVDL) KBP prediction models for coplanar VMAT to non-coplanar 4π radiotherapy plans.
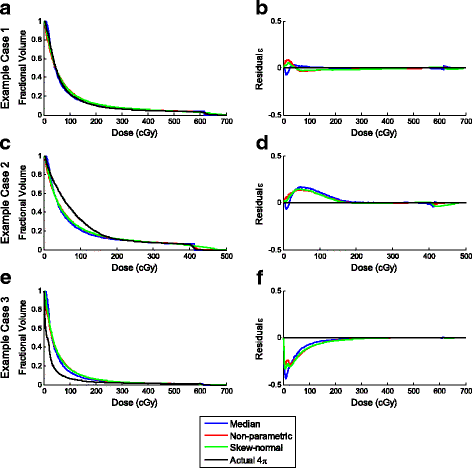
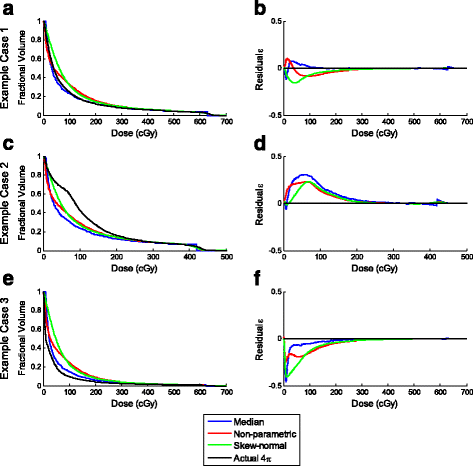
Methods: In this study, 21 liver SBRT cases were selected, which were initially treated using coplanar VMAT plans. They were then re-planned using 4π IMRT plans with 20 inversely optimized non-coplanar beams. OVH was calculated by expanding the planning target volume (PTV) and then plotting the percent overlap volume v with the liver vs. r v , the expansion distance. SVDL calculated the distance to the PTV for all liver voxels and bins the voxels of the same distance. Their dose information is approximated by either taking the median or using a skew-normal or non-parametric fit, which was then applied to voxels of unknown dose for each patient in a leave-one-out test. The liver volume receiving less than 15 Gy (V<15Gy), DVHs, and 3D dose distributions were predicted and compared between the prediction models and planning methods.
Results: On average, V<15Gy was predicted within 5%. SVDL was more accurate than OVH and able to predict DVH and 3D dose distributions. Median SVDL yielded predictive errors similar or lower than the fitting methods and is more computationally efficient. Prediction of the 4π dose was more accurate compared to VMAT for all prediction methods, with significant (p < 0.05) results except for OVH predicting liver V<15Gy (p = 0.063).
Conclusions: In addition to evaluating plan quality, KBP is useful to automatically determine the patient eligibility for liver SBRT and quantify the dosimetric gains from non-coplanar 4π plans. The two here analyzed dose prediction methods performed more accurately for the 4π plans than VMAT.
Figures




Similar articles
-
4π non-coplanar liver SBRT: a novel delivery technique.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013 Apr 1;85(5):1360-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2012.09.028. Epub 2012 Nov 12. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013. PMID: 23154076
-
Treatment planning comparison of IMPT, VMAT and 4π radiotherapy for prostate cases.Radiat Oncol. 2017 Jan 11;12(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s13014-016-0761-0. Radiat Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28077128 Free PMC article.
-
Integral dose investigation of non-coplanar treatment beam geometries in radiotherapy.Med Phys. 2014 Jan;41(1):011905. doi: 10.1118/1.4845055. Med Phys. 2014. PMID: 24387513
-
An improved distance-to-dose correlation for predicting bladder and rectum dose-volumes in knowledge-based VMAT planning for prostate cancer.Phys Med Biol. 2018 Jan 5;63(1):015035. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/aa9a30. Phys Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 29131812
-
Knowledge-based radiation treatment planning: A data-driven method survey.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2021 Aug;22(8):16-44. doi: 10.1002/acm2.13337. Epub 2021 Jul 7. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2021. PMID: 34231970 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Elective nodal irradiation with simultaneous integrated boost stereotactic body radiotherapy for pancreatic cancer: Analyses of planning feasibility and geometrically driven DVH prediction model.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2019 Feb;20(2):71-83. doi: 10.1002/acm2.12528. Epub 2019 Jan 13. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2019. PMID: 30636367 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Recent developments in non-coplanar radiotherapy.Br J Radiol. 2019 May;92(1097):20180908. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20180908. Epub 2019 Feb 1. Br J Radiol. 2019. PMID: 30694086 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Incorporating human and learned domain knowledge into training deep neural networks: A differentiable dose-volume histogram and adversarial inspired framework for generating Pareto optimal dose distributions in radiation therapy.Med Phys. 2020 Mar;47(3):837-849. doi: 10.1002/mp.13955. Epub 2019 Dec 29. Med Phys. 2020. PMID: 31821577 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Automated Treatment Planning.Semin Radiat Oncol. 2022 Oct;32(4):343-350. doi: 10.1016/j.semradonc.2022.06.004. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36202437 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Automation in intensity modulated radiotherapy treatment planning-a review of recent innovations.Br J Radiol. 2018 Dec;91(1092):20180270. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20180270. Epub 2018 Sep 4. Br J Radiol. 2018. PMID: 30074813 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

