Cardiothoracic Transplant Recipient Mycoplasma hominis: An Uncommon Infection with Probable Donor Transmission
- PMID: 28438507
- PMCID: PMC5440619
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2017.04.026
Cardiothoracic Transplant Recipient Mycoplasma hominis: An Uncommon Infection with Probable Donor Transmission
Abstract
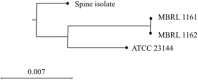
The role of infection with Mycoplasma hominis following cardiothoracic organ transplantation and its source of transmission have not been well-defined. Here, we identify and describe infection with M. hominis in patients following cardiothoracic organ transplantation after reviewing all cardiothoracic transplantations performed at our center between 1998 and July 2015. We found seven previously unreported cases of M. hominis culture positive infection all of whom presented with pleuritis, surgical site infection, and/or mediastinitis. PCR was used to establish the diagnosis in four cases. In two instances, paired single lung transplant recipients manifested infection, and in one of these pairs, isolates were indistinguishable by multilocus sequence typing (MLST). To investigate the prevalence of M. hominis in the lower respiratory tract, we tested 178 bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluids collected from immunocompromised subjects for M. hominis by PCR; all were negative. Review of the literature revealed an additional 15 cases of M. hominis in lung transplant recipients, most with similar clinical presentations to our cases. We recommend that M. hominis should be considered in post-cardiothoracic transplant infections presenting with pleuritis, surgical site infection, or mediastinitis. M. hominis PCR may facilitate early diagnosis and prompt therapy. Evaluation for possible donor transmission should be considered.
Keywords: Cardiothoracic transplantation; Infection; Mycoplasma hominis.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Abele-Horn M., Wolff C., Dressel P., Zimmermann A., Vahlensieck W., Pfaff F., Ruckdeschel G. Polymerase chain reaction versus culture for detection of Ureaplasma urealyticum and Mycoplasma hominis in the urogenital tract of adults and the respiratory tract of newborns. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1996;15:595–598. - PubMed
-
- Bharat A., Cunningham S.A., Scott Budinger G.R., Kreisel D., Dewet C.J., Gelman A.E., Waites K., Crabb D., Xiao L., Bhorade S., Ambalavanan N., Dilling D.F., Lowery E.M., Astor T., Hachem R., Krupnick A.S., Decamp M.M., Ison M.G., Patel R. Disseminated Ureaplasma infection as a cause of fatal hyperammonemia in humans. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015;7:284re3. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boyle E.M., Jr., Burdine J., Bolman R.M., III Successful treatment of Mycoplasma mediastinitis after heart-lung transplantation. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 1993;12:508–512. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

