IgG4-related disease presenting as posterior scleritis and vitritis, progressing to multifocal orbital involvement
- PMID: 28438752
- PMCID: PMC5534934
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2017-219568
IgG4-related disease presenting as posterior scleritis and vitritis, progressing to multifocal orbital involvement
Abstract
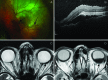
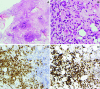
IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a rare, chronic inflammatory condition that may involve nearly every organ system. Originally identified as a cause of autoimmune pancreatitis, its characteristic histological and clinical features have been found in a wide variety of inflammatory presentations, including the eye and orbit. Here we describe an example of a case of IgG4-RD initially presenting as scleritis and vitritis, with further progression to multifocal bilateral orbital involvement. Tissue biopsy of an orbital mass was highly characteristic of IgG4-RD histology and a rapid clinical response to corticosteroids was observed. This case highlights IgG4-RD as a rare cause of intraocular inflammation that may progress to involve the orbit.
Keywords: Immunology; Ophthalmology; Retina; Rheumatology.
© BMJ Publishing Group Ltd (unless otherwise stated in the text of the article) 2017. All rights reserved. No commercial use is permitted unless otherwise expressly granted.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
