Intraductal oncocytic papillary neoplasm: a benign hepatic cystic neoplasm
- PMID: 28438794
- PMCID: PMC5534910
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2016-218139
Intraductal oncocytic papillary neoplasm: a benign hepatic cystic neoplasm
Abstract
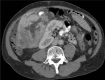
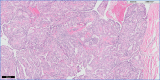
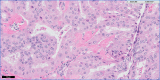
A 61-year-old Asian man presented with severe right upper quadrant pain which had been worsening for several months. Laboratory results indicated elevated aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase. The subsequent ultrasound, CT and MRI showed a large cystic mass with solid components and severe intrahepatic and extrahepatic biliary ductal dilatation. The mass was resected and pathology showed a well-demarcated mucinous cystic lesion with polygonal cells containing ovoid nuclei and abundant pink oncocytic cytoplasm. These findings are characteristic of intraductal oncocytic papillary neoplasm (IOPN), a rare subtype of intraductal papillary neoplasm of the liver. IOPN occurs most frequently in the Asian regions endemic to clonorchiasis and hepatolithiasis; however, cases have been reported in the Western world as well. Patients with IOPN are male or female and typically middle-aged. Treatment is typically resection. Prognosis is favourable and recurrence is rare. The 5-year survival rate is upwards of 80%.
Keywords: Gastroenterology; Liver disease; Radiology.
© BMJ Publishing Group Ltd (unless otherwise stated in the text of the article) 2017. All rights reserved. No commercial use is permitted unless otherwise expressly granted.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Intraductal oncocytic papillary neoplasm of the bile duct: clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical characteristics of 6 cases.Hum Pathol. 2009 Nov;40(11):1543-52. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2009.03.014. Epub 2009 Jun 21. Hum Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19540556
-
Intraductal oncocytic papillary neoplasm of the extrahepatic bile duct: report of a case.Surg Today. 2012 Dec;42(12):1240-3. doi: 10.1007/s00595-012-0233-6. Epub 2012 Jun 28. Surg Today. 2012. PMID: 22739752
-
Intraductal oncocytic papillary neoplasm of the extrahepatic biliary tree: first report.Am Surg. 2004 Jan;70(1):55-8. Am Surg. 2004. PMID: 14964549
-
[Intraductal papillary neoplasms of the bile duct (IPNB). Diagnostic criteria, carcinogenesis and differential diagnostics].Pathologe. 2013 Nov;34 Suppl 2:235-40. doi: 10.1007/s00292-013-1861-3. Pathologe. 2013. PMID: 24196621 Review. German.
-
Intraductal papillary mucininous neoplasm of the bile ducts: multimodality assessment with pathologic correlation.Abdom Imaging. 2011 Aug;36(4):447-56. doi: 10.1007/s00261-010-9649-x. Abdom Imaging. 2011. PMID: 20959978 Review.
Cited by
-
A missed case of intraductal oncocytic papillary neoplasm associated with missed stones in extrahepatic bile duct: a case report.Front Oncol. 2024 May 21;14:1349914. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1349914. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38841165 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
