MeCP2-regulated miRNAs control early human neurogenesis through differential effects on ERK and AKT signaling
- PMID: 28439102
- PMCID: PMC5815944
- DOI: 10.1038/mp.2017.86
MeCP2-regulated miRNAs control early human neurogenesis through differential effects on ERK and AKT signaling
Abstract
Rett syndrome (RTT) is an X-linked, neurodevelopmental disorder caused primarily by mutations in the methyl-CpG-binding protein 2 (MECP2) gene, which encodes a multifunctional epigenetic regulator with known links to a wide spectrum of neuropsychiatric disorders. Although postnatal functions of MeCP2 have been thoroughly investigated, its role in prenatal brain development remains poorly understood. Given the well-established importance of microRNAs (miRNAs) in neurogenesis, we employed isogenic human RTT patient-derived induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) and MeCP2 short hairpin RNA knockdown approaches to identify novel MeCP2-regulated miRNAs enriched during early human neuronal development. Focusing on the most dysregulated miRNAs, we found miR-199 and miR-214 to be increased during early brain development and to differentially regulate extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)/mitogen-activated protein kinase and protein kinase B (PKB/AKT) signaling. In parallel, we characterized the effects on human neurogenesis and neuronal differentiation brought about by MeCP2 deficiency using both monolayer and three-dimensional (cerebral organoid) patient-derived and MeCP2-deficient neuronal culture models. Inhibiting miR-199 or miR-214 expression in iPSC-derived neural progenitors deficient in MeCP2 restored AKT and ERK activation, respectively, and ameliorated the observed alterations in neuronal differentiation. Moreover, overexpression of miR-199 or miR-214 in the wild-type mouse embryonic brains was sufficient to disturb neurogenesis and neuronal migration in a similar manner to Mecp2 knockdown. Taken together, our data support a novel miRNA-mediated pathway downstream of MeCP2 that influences neurogenesis via interactions with central molecular hubs linked to autism spectrum disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
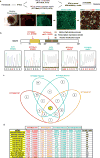
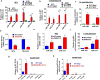
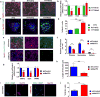
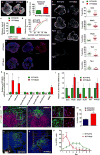
Similar articles
-
miR-199a Links MeCP2 with mTOR Signaling and Its Dysregulation Leads to Rett Syndrome Phenotypes.Cell Rep. 2015 Sep 22;12(11):1887-901. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.08.028. Epub 2015 Sep 3. Cell Rep. 2015. PMID: 26344767
-
MicroRNA-212-3p regulates early neurogenesis through the AKT/mTOR pathway by targeting MeCP2.Neurochem Int. 2020 Jul;137:104734. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2020.104734. Epub 2020 Apr 1. Neurochem Int. 2020. PMID: 32246981
-
Quantitative proteomic analysis of Rett iPSC-derived neuronal progenitors.Mol Autism. 2020 May 27;11(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s13229-020-00344-3. Mol Autism. 2020. PMID: 32460858 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling Rett Syndrome Using Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2016;15(5):544-50. doi: 10.2174/1871527315666160413120156. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2016. PMID: 27071793 Review.
-
MeCP2 expression and function during brain development: implications for Rett syndrome's pathogenesis and clinical evolution.Brain Dev. 2005 Nov;27 Suppl 1:S77-S87. doi: 10.1016/j.braindev.2004.10.008. Epub 2005 Sep 22. Brain Dev. 2005. PMID: 16182491 Review.
Cited by
-
Modeling neurological disorders using brain organoids.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Mar;111:4-14. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2020.05.026. Epub 2020 Jun 17. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 32561297 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting TGF-β signal transduction for fibrosis and cancer therapy.Mol Cancer. 2022 Apr 23;21(1):104. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01569-x. Mol Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35461253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-197 controls ADAM10 expression to mediate MeCP2's role in the differentiation of neuronal progenitors.Cell Death Differ. 2019 Oct;26(10):1863-1879. doi: 10.1038/s41418-018-0257-6. Epub 2018 Dec 18. Cell Death Differ. 2019. PMID: 30560934 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling human neurodevelopmental diseases with brain organoids.Cell Regen. 2022 Jan 4;11(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s13619-021-00103-6. Cell Regen. 2022. PMID: 34982276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Patient-Derived Stem Cells, Another in vitro Model, or the Missing Link Toward Novel Therapies for Autism Spectrum Disorders?Front Pediatr. 2019 Jun 6;7:225. doi: 10.3389/fped.2019.00225. eCollection 2019. Front Pediatr. 2019. PMID: 31245336 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Krol J, Loedige I, Filipowicz W. The widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay. Nat Rev Genet. 2010;11:597–610. - PubMed
-
- Coolen M, Bally-Cuif L. MicroRNAs in brain development and physiology. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2009;19:461–470. - PubMed
-
- Amir RE, Van den Veyver IB, Wan M, Tran CQ, Francke U, Zoghbi HY. Rett syndrome is caused by mutations in X-linked MECP2, encoding methyl-CpG-binding protein 2. Nat Genet. 1999;23:185–188. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

