Prevalence of low back pain in adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis: a systematic review
- PMID: 28439404
- PMCID: PMC5399433
- DOI: 10.1186/s12998-017-0143-1
Prevalence of low back pain in adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis: a systematic review
Abstract
Background: Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis is the most common spinal deformity occurring in adolescents and its established prevalence varies from 2 to 3%. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis has been identified as a potential risk factor for the development of low back pain in adolescents. The purpose of this study was to systematically review studies of the prevalence of low back pain in adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis in order to establish the quality of the evidence and determine whether the prevalence estimates could be statistically pooled.
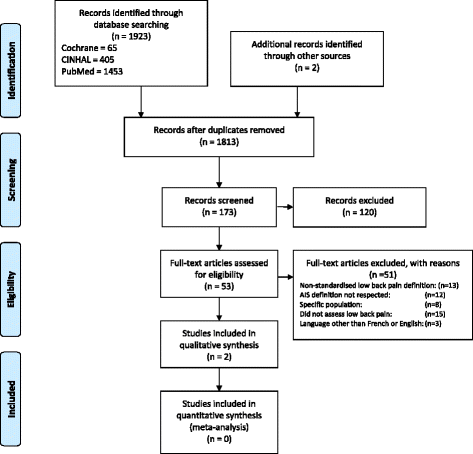
Methods: Systematic electronic searches were undertaken in PubMed, CINAHL, and CENTRAL without any restrictions. Studies were eligible for inclusion if they reported the prevalence of low back pain in adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis. Studies were excluded if they detailed the prevalence of pain in post-surgical subjects or were published in languages other than English or French. Data were reported qualitatively, since there was insufficient evidence for statistical pooling.
Results: The electronic search strategies yielded 1811 unique studies. Only two studies fulfilled the eligibility criteria. The prevalence of low back pain in adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis ranged from 34.7 to 42.0%. However, these prevalence estimates should be viewed cautiously as the included studies were at high risk of bias.
Conclusion: The results of this systematic review indicate that adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis frequently experience low back pain. However, there was insufficient evidence to confidently estimate low back pain prevalence in adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis and further studies are needed in this area.
Keywords: Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis; Low back pain; Prevalence.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tracking low back pain in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: a prospective cohort study protocol.Chiropr Man Therap. 2017 Sep 5;25:22. doi: 10.1186/s12998-017-0155-x. eCollection 2017. Chiropr Man Therap. 2017. PMID: 28878881 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term follow-up of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients who had Harrington instrumentation and fusion to the lower lumbar vertebrae: is low back pain a problem?Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009 Nov 15;34(24):E873-8. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181aa7d53. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009. PMID: 19910755
-
Comparative multifactorial analysis of the effects of idiopathic adolescent scoliosis and Scheuermann kyphosis on the self-perceived health status of adolescents treated with brace.Eur Spine J. 2007 Apr;16(4):537-46. doi: 10.1007/s00586-006-0214-9. Epub 2006 Sep 5. Eur Spine J. 2007. PMID: 16953447 Free PMC article.
-
Back pain in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: A comprehensive review.J Child Orthop. 2023 Feb 3;17(2):126-140. doi: 10.1177/18632521221149058. eCollection 2023 Apr. J Child Orthop. 2023. PMID: 37034188 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Idiopathic scoliosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of heritability.EFORT Open Rev. 2022 May 31;7(6):414-421. doi: 10.1530/EOR-22-0026. EFORT Open Rev. 2022. PMID: 35638601 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of Mis-Selection of End Vertebrae and Its Effect on Measuring Cobb Angle and Curve Length in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis.J Clin Med. 2024 Aug 5;13(15):4562. doi: 10.3390/jcm13154562. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39124828 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factors for proximal junctional kyphosis in a multicenter study of Lenke type 5 and 6 adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients.Spine Deform. 2024 Jan;12(1):173-180. doi: 10.1007/s43390-023-00762-2. Epub 2023 Sep 1. Spine Deform. 2024. PMID: 37656391
-
Research trends of biomechanics in scoliosis from 1999 to 2023: a bibliometric analysis.Spine Deform. 2025 Mar;13(2):391-403. doi: 10.1007/s43390-024-01000-z. Epub 2024 Nov 5. Spine Deform. 2025. PMID: 39499450 Review.
-
How Common Is Back Pain and What Biopsychosocial Factors Are Associated With Back Pain in Patients With Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2019 Apr;477(4):676-686. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000000569. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2019. PMID: 30516661 Free PMC article.
-
Content validity of the Scoliosis Research Society questionnaire (SRS-22r): A qualitative concept elicitation study.PLoS One. 2023 May 5;18(5):e0285538. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0285538. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37146069 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vos T, Flaxman AD, Naghavi M, Lozano R, Michaud C, Ezzati M, Shibuya K, Salomon JA, Abdalla S, Aboyans V, et al. Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet. 2010;380(9859):2163–2196. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61729-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical