A Comparison of the Effects of 20% Mannitol and 3% NaCl on Coagulation Parameters In Vitro using ROTEM: A Prospective Randomized Crossover Study
- PMID: 28439440
- PMCID: PMC5396905
- DOI: 10.5152/TJAR.2017.74875
A Comparison of the Effects of 20% Mannitol and 3% NaCl on Coagulation Parameters In Vitro using ROTEM: A Prospective Randomized Crossover Study
Abstract
Objective: The aim of the present study is to compare the effect of 20% mannitol and 3% NaCl on blood coagulation in vitro using rotational thromboelastometry (ROTEM).
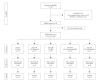
Methods: Twenty-millilitre blood samples were obtained from 15 volunteers. In each group, 2 mL blood samples were collected into both polypropylene tubes and EDTA tubes for ROTEM and hemogram analysis. After sampling, blood samples were diluted with test solutions. Group C (control): Only blood, Group M (mannitol): 7% vol 20% mannitol concentration in the blood, Group hypertonic saline (HS): 7% vol 3% hypertonic saline (NaCl) in the blood, Group M/H (mannitol and hydroxyethyl starch solutions [HES]): 6% vol 20% mannitol concentration and 8% vol HES in the blood and Group HS/H (hypertonic saline and HES): 6% vol 3% hypertonic saline concentration and 8% vol HES in the blood. The following thromboelastometric parameters were measured automatically: clotting time (CT) and clot formation time (CFT) with intrinsic activation by tissue factor (InTEM), CT, CFT and maximum clot firmness (MCF) with extrinsic activation by tissue factor (ExTEM) and MCF with FibTEM.
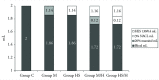
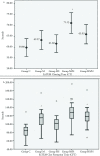
Results: The ExTEM CT value was found to be significantly longer in the M/H group than in the controls. The ExTEM CFT median and percentile values were: group C: 85 s (70-95 s), group M: 115 s (94-128 s), group HS: 102 s (84-114 s), group M/H: 128 s (110-144 s) and group HS/H: 118 s (107-132 s). In all the groups, FibTEM MCF values were significantly lower than the control and also there was a significant difference between groups M and HS according to FibTEM MCF values.
Conclusion: Whole-blood coagulation disorder induced by these solutions is mainly dependent on fibrinogen and fibrin interaction. However, 3% HS has much less negative effect on coagulation.
Keywords: 20% mannitol; 3% NaCl; coagulation; neuroanaesthesia.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: No conflict of interest was declared by the authors.
Figures

Comment in
-
Comment on: A Comparison of the Effects of 20% Mannitol and 3% NaCl on Coagulation Parameters In Vitro using ROTEM: A Prospective Randomized Crossover Study.Turk J Anaesthesiol Reanim. 2018 Feb;46(1):70. doi: 10.5152/TJAR.2018.95777. Epub 2018 Feb 1. Turk J Anaesthesiol Reanim. 2018. PMID: 30140506 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Comparison of the in vitro effects of saline, hypertonic hydroxyethyl starch, hypertonic saline, and two forms of hydroxyethyl starch on whole blood coagulation and platelet function in dogs.J Vet Emerg Crit Care (San Antonio). 2015 Jul-Aug;25(4):474-87. doi: 10.1111/vec.12320. Epub 2015 Jun 2. J Vet Emerg Crit Care (San Antonio). 2015. PMID: 26037241
-
Equiosmolar Solutions of Hypertonic Saline and Mannitol Do Not Impair Blood Coagulation During Elective Intracranial Surgery.J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2017 Jan;29(1):8-13. doi: 10.1097/ANA.0000000000000255. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2017. PMID: 26580123 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of hypertonic saline and mannitol on whole blood coagulation in vitro assessed by thromboelastometry.Neurocrit Care. 2011 Apr;14(2):238-43. doi: 10.1007/s12028-010-9475-6. Neurocrit Care. 2011. PMID: 21369792
-
The influence of laboratory coagulation tests and clotting factor levels on Rotation Thromboelastometry (ROTEM(R)) during major surgery with hemorrhage.Anesth Analg. 2013 Aug;117(2):314-21. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e31829569ac. Epub 2013 Jun 18. Anesth Analg. 2013. PMID: 23780419
-
Hypocoagulability and Platelet Dysfunction Are Exacerbated by Synthetic Colloids in a Canine Hemorrhagic Shock Model.Front Vet Sci. 2018 Nov 13;5:279. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2018.00279. eCollection 2018. Front Vet Sci. 2018. PMID: 30483517 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Comment on: A Comparison of the Effects of 20% Mannitol and 3% NaCl on Coagulation Parameters In Vitro using ROTEM: A Prospective Randomized Crossover Study.Turk J Anaesthesiol Reanim. 2018 Feb;46(1):70. doi: 10.5152/TJAR.2018.95777. Epub 2018 Feb 1. Turk J Anaesthesiol Reanim. 2018. PMID: 30140506 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The Complex Process of Haemostasis and Interactions due to Hyperosmotic Fluids.Turk J Anaesthesiol Reanim. 2017 Apr;45(2):83-84. doi: 10.5152/TJAR.2017.290317. Epub 2017 Apr 1. Turk J Anaesthesiol Reanim. 2017. PMID: 28439438 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Mannitol and the Combination of Mannitol and Gelatin Impair Whole Blood Coagulation and the Platelet Function In Vitro.Turk J Anaesthesiol Reanim. 2019 Jun;47(3):199-205. doi: 10.5152/TJAR.2019.86300. Epub 2019 Feb 19. Turk J Anaesthesiol Reanim. 2019. PMID: 31183466 Free PMC article.
-
Examining the Effect of Hypertonic Saline Administered for Reduction of Intracranial Hypertension on Coagulation.J Am Coll Surg. 2020 Mar;230(3):322-330.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2019.11.011. Epub 2019 Dec 14. J Am Coll Surg. 2020. PMID: 31843691 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Luostarinen T, Niiya T, Schramko A, Rosenberg P, Niemi T. Comparison of hypertonic saline and mannitol on whole blood coagulation in vitro assessed by thromboelastometry. Neurocrit Care. 2011;14:238–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12028-010-9475-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- The Brain Trauma Foundation. The American Association of Neurological Surgeons. The Joint Section on Neurotrauma and Critical Care. Initial management. J Neurotrauma. 2000;17:463–9. - PubMed
-
- Schwarz S, Schwab S, Bertram M, Aschoff A, Hacke W. Effects of hypertonic saline hydroxyethyl starch solution and mannitol in patients with increased intracranial pressure after stroke. Stroke. 1998;29:1550–5. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.29.8.1550. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Harutjunyan L, Holz C, Rieger A, Menzel M, Grond S, Soukup J. Efficiency of 7.2% hypertonic saline hydroxyethyl starch 200/0.5 versus mannitol 15% in the treatment of increased intracranial pressure in neurosurgical patients: A randomized clinical trial. Crit Care. 2005;9:530–40. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc3767. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rozet I, Tontisirin N, Muangman S, Vavilala MS, Souter MJ, Lee LA, et al. Effect of equiosmolar solutions of mannitol versus hypertonic saline on intraoperative brain relaxation and electrolyte balance. Anesthesiology. 2007;107:697–704. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.anes.0000286980.92759.94. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
