Chronic Toxoplasma gondii Infection Exacerbates Secondary Polymicrobial Sepsis
- PMID: 28439500
- PMCID: PMC5383667
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00116
Chronic Toxoplasma gondii Infection Exacerbates Secondary Polymicrobial Sepsis
Abstract
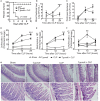
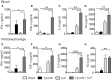
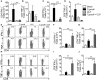
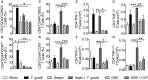
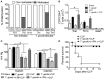
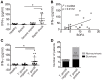
Sepsis is a severe syndrome that arises when the host response to an insult is exacerbated, leading to organ failure and frequently to death. How a chronic infection that causes a prolonged Th1 expansion affects the course of sepsis is unknown. In this study, we showed that mice chronically infected with Toxoplasma gondii were more susceptible to sepsis induced by cecal ligation and puncture (CLP). Although T. gondii-infected mice exhibited efficient control of the bacterial burden, they showed increased mortality compared to the control groups. Mechanistically, chronic T. gondii infection induces the suppression of Th2 lymphocytes via Gata3-repressive methylation and simultaneously induces long-lived IFN-γ-producing CD4+ T lymphocytes, which promotes systemic inflammation that is harmful during CLP. Chronic T. gondii infection intensifies local and systemic Th1 cytokines as well as nitric oxide production, which reduces systolic and diastolic arterial blood pressures after sepsis induction, thus predisposing the host to septic shock. Blockade of IFN-γ prevented arterial hypotension and prolonged the host lifespan by reducing the cytokine storm. Interestingly, these data mirrored our observation in septic patients, in which sepsis severity was positively correlated to increased levels of IFN-γ in patients who were serologically positive for T. gondii. Collectively, these data demonstrated that chronic infection with T. gondii is a critical factor for sepsis severity that needs to be considered when designing strategies to prevent and control the outcome of this devastating disease.
Keywords: Toxoplasma gondii; chronic disease; coinfection; sepsis; septic shock.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Toxoplasma Co-infection Prevents Th2 Differentiation and Leads to a Helminth-Specific Th1 Response.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Jul 25;7:341. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00341. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28791259 Free PMC article.
-
Infection with Toxoplasma gondii reduces established and developing Th2 responses induced by Nippostrongylus brasiliensis infection.Infect Immun. 2004 Jul;72(7):3812-22. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.7.3812-3822.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 15213122 Free PMC article.
-
[Rudolf-Virchow Prize 1998. Award lecture. Toxoplasmosis: a model infection for studying systemic and intracerebral immune reactions].Verh Dtsch Ges Pathol. 1998;82:9-22. Verh Dtsch Ges Pathol. 1998. PMID: 10095413 German.
-
DNA immunization with eukaryotic initiation factor-2α of Toxoplasma gondii induces protective immunity against acute and chronic toxoplasmosis in mice.Vaccine. 2013 Dec 16;31(52):6225-31. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.10.034. Epub 2013 Oct 31. Vaccine. 2013. PMID: 24183979
-
Mechanisms of innate resistance to Toxoplasma gondii infection.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1997 Sep 29;352(1359):1355-9. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1997.0120. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1997. PMID: 9355127 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Toxoplasma gondii and Trypanosoma lewisi Infection in Urban Small Mammals From Cotonou, Benin, With Special Emphasis on Coinfection Patterns.Transbound Emerg Dis. 2025 Feb 14;2025:9976509. doi: 10.1155/tbed/9976509. eCollection 2025. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2025. PMID: 40302764 Free PMC article.
-
The role of Curcuma longa essential oil in controlling acute toxoplasmosis by improving the immune system and reducing inflammation and oxidative stress.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Apr 27;13:1161133. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1161133. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37249978 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro and in vivo Anti-Toxoplasma Effects of Allium sativum Essential Oil Against Toxoplasma gondii RH Strain.Infect Drug Resist. 2021 Nov 30;14:5057-5068. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S337905. eCollection 2021. Infect Drug Resist. 2021. PMID: 34876824 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Potential and Safety of the Cinnamomum zeylanicum Methanolic Extract Against Chronic Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Mice.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Jun 9;12:900046. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.900046. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35755846 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Toxoplasma activity of silver nanoparticles green synthesized with Phoenix dactylifera and Ziziphus spina-christi extracts which inhibits inflammation through liver regulation of cytokines in Balb/c mice.Biosci Rep. 2019 May 15;39(5):BSR20190379. doi: 10.1042/BSR20190379. Print 2019 May 31. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30992387 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andrade W. A., Souza M. C., Ramos-Martinez E., Nagpal K., Dutra M. S., Melo M. B., et al. . (2013). Combined action of nucleic acid-sensing Toll-like receptors and TLR11/TLR12 heterodimers imparts resistance to Toxoplasma gondii in mice. Cell Host Microbe 13, 42–53. 10.1016/j.chom.2012.12.003 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benevides L., Milanezi C. M., Yamauchi L. M., Benjamim C. F., Silva J. S., Silva N. M. (2008). CCR2 receptor is essential to activate microbicidal mechanisms to control Toxoplasma gondii infection in the central nervous system. Am. J. Pathol. 173, 741–751. 10.2353/ajpath.2008.080129 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

