WIP1 phosphatase as pharmacological target in cancer therapy
- PMID: 28439615
- PMCID: PMC5442293
- DOI: 10.1007/s00109-017-1536-2
WIP1 phosphatase as pharmacological target in cancer therapy
Abstract
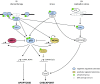
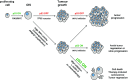
DNA damage response (DDR) pathway protects cells from genome instability and prevents cancer development. Tumor suppressor p53 is a key molecule that interconnects DDR, cell cycle checkpoints, and cell fate decisions in the presence of genotoxic stress. Inactivating mutations in TP53 and other genes implicated in DDR potentiate cancer development and also influence the sensitivity of cancer cells to treatment. Protein phosphatase 2C delta (referred to as WIP1) is a negative regulator of DDR and has been proposed as potential pharmaceutical target. Until recently, exploitation of WIP1 inhibition for suppression of cancer cell growth was compromised by the lack of selective small-molecule inhibitors effective at cellular and organismal levels. Here, we review recent advances in development of WIP1 inhibitors and discuss their potential use in cancer treatment.
Keywords: Cancer; Checkpoint; DNA damage response; Inhibitor; Phosphatase; p53.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
WIP1 Promotes Homologous Recombination and Modulates Sensitivity to PARP Inhibitors.Cells. 2019 Oct 15;8(10):1258. doi: 10.3390/cells8101258. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31619012 Free PMC article.
-
Wee1 inhibition potentiates Wip1-dependent p53-negative tumor cell death during chemotherapy.Cell Death Dis. 2016 Apr 14;7(4):e2195. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.96. Cell Death Dis. 2016. PMID: 27077811 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of WIP1 phosphatase sensitizes breast cancer cells to genotoxic stress and to MDM2 antagonist nutlin-3.Oncotarget. 2016 Mar 22;7(12):14458-75. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7363. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26883108 Free PMC article.
-
Wip1 phosphatase: between p53 and MAPK kinases pathways.Oncotarget. 2016 May 24;7(21):31563-71. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7325. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26883196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of PPM1D in cancer and advances in studies of its inhibitors.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 May;125:109956. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.109956. Epub 2020 Jan 29. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 32006900 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Discovery of a cryptic pocket in the AI-predicted structure of PPM1D phosphatase explains the binding site and potency of its allosteric inhibitors.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Mar 24:2023.03.22.533829. doi: 10.1101/2023.03.22.533829. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Apr 18;10:1171143. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1171143. PMID: 36993233 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Beyond Cisplatin: Combination Therapy with Arsenic Trioxide.Inorganica Chim Acta. 2019 Oct 1;496:119030. doi: 10.1016/j.ica.2019.119030. Epub 2019 Jul 24. Inorganica Chim Acta. 2019. PMID: 32863421 Free PMC article.
-
PPM1D/Wip1 is amplified, overexpressed, and mutated in human non-Hodgkin's lymphomas.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Nov 4;51(1):1115. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-10029-2. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39489796
-
Release of CHK-2 from PPM-1.D anchorage schedules meiotic entry.Sci Adv. 2022 Feb 18;8(7):eabl8861. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abl8861. Epub 2022 Feb 16. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 35171669 Free PMC article.
-
Cell confluency affects p53 dynamics in response to DNA damage.Mol Biol Cell. 2025 Jun 1;36(6):br16. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E24-09-0394. Epub 2025 Apr 9. Mol Biol Cell. 2025. PMID: 40202833
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

