Phase II Study of the Efficacy and Safety of Pembrolizumab for Relapsed/Refractory Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma
- PMID: 28441111
- PMCID: PMC5791843
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2016.72.1316
Phase II Study of the Efficacy and Safety of Pembrolizumab for Relapsed/Refractory Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma
Abstract
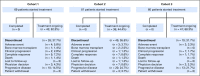
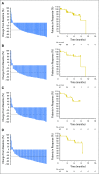
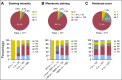
Purpose Hodgkin Reed-Sternberg cells harbor alterations in chromosome 9p24.1, leading to overexpression of programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) and PD-L2. Pembrolizumab, a programmed death 1-blocking antibody, demonstrated a high overall response rate (ORR) in patients with relapsed or refractory classic Hodgkin lymphoma (rrHL) in phase I testing. Methods KEYNOTE-087 ( ClinicalTrials.gov identifier, NCT02453594) was a single-arm phase II study of pembrolizumab in three cohorts of patients with rrHL, defined on the basis of lymphoma progression after (1) autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) and subsequent brentuximab vedotin (BV); (2) salvage chemotherapy and BV, and thus, ineligible for ASCT because of chemoresistant disease; and (3) ASCT, but without BV after transplantation. Patients received pembrolizumab 200 mg once every 3 weeks. Response was assessed every 12 weeks. The primary end points were ORR by central review and safety. Results A total of 210 patients were enrolled and treated (69 in cohort 1, 81 in cohort 2, and 60 in cohort 3). At the time of analysis, patients received a median of 13 treatment cycles. Per central review, the ORR was 69.0% (95% CI, 62.3% to 75.2%), and the complete response rate was 22.4% (95% CI, 16.9% to 28.6%). By cohort, ORRs were 73.9% for cohort 1, 64.2% for cohort 2, and 70.0% for cohort 3. Thirty-one patients had a response ≥ 6 months. The safety profile was largely consistent with previous pembrolizumab studies. Conclusion Pembrolizumab was associated with high response rates and an acceptable safety profile in patients with rrHL, offering a new treatment paradigm for this disease.
Figures
References
-
- Engert A, Raemaekers J. Treatment of early-stage Hodgkin lymphoma. Semin Hematol. 2016;53:165–170. - PubMed
-
- Vassilakopoulos TP, Johnson PW. Treatment of advanced-stage Hodgkin lymphoma. Semin Hematol. 2016;53:171–179. - PubMed
-
- Kuruvilla J. Standard therapy of advanced Hodgkin lymphoma. Hematology (Am Soc Hematol Educ Program) 2009;2009:497–506. - PubMed
-
- Kuruvilla J, Keating A, Crump M. How I treat relapsed and refractory Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood. 2011;117:4208–4217. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

