Preoperative clinical pathway of breast cancer patients: determinants of compliance with EUSOMA quality indicators
- PMID: 28441385
- PMCID: PMC5520093
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2017.114
Preoperative clinical pathway of breast cancer patients: determinants of compliance with EUSOMA quality indicators
Abstract
Background: The European Society of Breast Cancer Specialists (EUSOMA) has defined quality indicators for breast cancer (BC). The aim of this study was to describe the preoperative clinical pathway of breast cancer patients and evaluate the determinants of compliance with EUSOMA quality indicators in the Optisoins01 cohort.
Methods: Optisoins01 is a prospective, multicentric study. Data from operable BC patients were collected, including results from before surgery to 1 year follow-up. Seven preoperative EUSOMA quality indicators were compared with the clinical pathways Optisoins01.
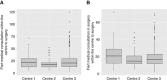
Results: Six hundred and four patients were included. European Society of Breast Cancer Specialists targets were reached for indicator 1 (completeness of clinical and imaging diagnostic work-up), 3 (preoperative definitive diagnosis) and 5 (waiting time). For indicator 8 (multidisciplinary discussion), the minimum standard of 90% of the patients was reached only in general hospitals and comprehensive cancer centres. Having more than 1 medical examination within the centre was associated with an increased waiting time for surgery, whereas it was reduced by having an outpatient breast biopsy. The comprehensive cancer centre type was the only parameter associated with the other quality indicators.
Conclusions: European Society of Breast Cancer Specialists quality indicators are a useful tool to evaluate care organisations. This study highlights the need for a standardised and coordinated preoperative clinical pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Arndt V, Stürmer T, Stegmaier C, Ziegler H, Becker A, Brenner H (2003) Provider delay among patients with breast cancer in Germany: a population-based study. J Clin Oncol 21: 1440–1446. - PubMed
-
- Ayrault-Piault S, Grosclaude P, Daubisse-Marliac L, Pascal J, Leux C, Fournier E, Tagri AD, Métais M, Lombrail P, Woronoff AS, Molinié F (2016) Are disparities of waiting times for breast cancer care related to socio-economic factors? A regional population-based study (France). Int J Cancer 139: 1983–1993. - PubMed
-
- Baliski C, McGahan CE, Liberto CM, Broughton S, Ellard S, Taylor M, Bates J, Lai A (2014) Influence of nurse navigation on wait times for breast cancer care in a Canadian regional cancer center. Am J Surg 207: 686–691, discussion 691–692. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical