Suppression of Oxidative Stress and NFκB/MAPK Signaling by Lyophilized Black Raspberries for Esophageal Cancer Prevention in Rats
- PMID: 28441719
- PMCID: PMC5409752
- DOI: 10.3390/nu9040413
Suppression of Oxidative Stress and NFκB/MAPK Signaling by Lyophilized Black Raspberries for Esophageal Cancer Prevention in Rats
Abstract
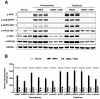
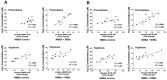
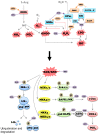
Research in the laboratory has shown that lyophilized black raspberries (BRB) significantly inhibit N-nitrosomethylbenzylamine (NMBA)-induced esophageal squamous cell carcinogenesis in rats. The objective of the present study is to characterize the underlying mechanism(s) of anti-cancer action of BRB in this preclinical animal model focusing on oxidative stress and its related oncogenic signaling pathways. Esophageal epithelial tissues were collected and assessed for markers of oxidative stress and nuclear factor κB (NFκB) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK). BRB reduced the incidence of esophageal cancer from 100% in NMBA-treated rats to 81.5% in rats treated with NMBA plus BRB (p < 0.05). Tumor multiplicity was reduced from 4.73 ± 0.45 tumors per esophagus in NMBA-treated rats to 1.44 ± 0.26 in rats treated with NMBA plus BRB (p < 0.001). The data indicated that NMBA treatment increased production of hydrogen peroxide and lipid hydroperoxide, reduced expression and activity of glutathione peroxidase and superoxide dismutase 2, and activated NFκB/MAPK signaling in rat esophagus. The study's results show that BRB reverses oxidative stress and suppresses NFκB/MAPK pathways, which could be the mechanisms for esophageal cancer chemopreventive action of BRB in rats.
Keywords: MAPK; NFκB; black raspberries; esophageal cancer; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Chemopreventive properties of black raspberries in N-nitrosomethylbenzylamine-induced rat esophageal tumorigenesis: down-regulation of cyclooxygenase-2, inducible nitric oxide synthase, and c-Jun.Cancer Res. 2006 Mar 1;66(5):2853-9. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3279. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 16510608 Free PMC article.
-
Black raspberries inhibit N-nitrosomethylbenzylamine (NMBA)-induced angiogenesis in rat esophagus parallel to the suppression of COX-2 and iNOS.Carcinogenesis. 2006 Nov;27(11):2301-7. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgl109. Epub 2006 Jun 15. Carcinogenesis. 2006. PMID: 16777990
-
Protection against esophageal cancer in rodents with lyophilized berries: potential mechanisms.Nutr Cancer. 2006;54(1):33-46. doi: 10.1207/s15327914nc5401_5. Nutr Cancer. 2006. PMID: 16800771 Free PMC article.
-
Esophageal carcinogenesis in the rat: a model for aerodigestive tract cancer.J Cell Biochem Suppl. 1993;17F:91-4. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240531013. J Cell Biochem Suppl. 1993. PMID: 8412212 Review.
-
[Natural compounds in chemoprevention of esophageal squamous cell tumors--experimental studies].Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2009 Feb;26(152):156-61. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2009. PMID: 19388525 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Systems Pharmacology and Microbiome Dissection of Shen Ling Bai Zhu San Reveal Multiscale Treatment Strategy for IBD.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Jun 23;2019:8194804. doi: 10.1155/2019/8194804. eCollection 2019. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019. PMID: 31341536 Free PMC article.
-
Anthocyanins in Colorectal Cancer Prevention Review.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Oct 12;10(10):1600. doi: 10.3390/antiox10101600. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34679735 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemopreventive Properties of Black Raspberries and Strawberries in Esophageal Cancer Review.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Sep 15;11(9):1815. doi: 10.3390/antiox11091815. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36139889 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic Regulation of Glycolysis and AMP Activated Protein Kinase Pathways during Black Raspberry-Mediated Oral Cancer Chemoprevention.Metabolites. 2019 Jul 11;9(7):140. doi: 10.3390/metabo9070140. Metabolites. 2019. PMID: 31336728 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of esophageal cancer growth through the suppression of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Sep 17;12:7637-7647. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S205457. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 31571914 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Trivers K.F., Sabatino S.A., Stewart S.L. Trends in esophageal cancer incidence by histology, United States, 1998–2003. Int. J. Cancer. 2008;123:1422–1428. - PubMed
-
- Yamashita K., Upadhyay S., Osada M., Hoque M.O., Xiao Y., Mori M., Sato F., Meltzer S.J., Sidransky D. Pharmacologic unmasking of epigenetically silenced tumor suppressor genes in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 2002;2:485–495. - PubMed
-
- Chestnov O. Who Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic, 2013: Enforcing Bans on Tobacco Advertising, Promotion and Sponsorship. World Health Orgnization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2013. pp. 11–89.
-
- Kresty L.A., Morse M.A., Morgan C., Carlton P.S., Lu J., Gupta A., Blackwood M., Stoner G.D. Chemoprevention of esophageal tumorigenesis by dietary administration of lyophilized black raspberries. Cancer Res. 2001;61:6112–6119. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

