Peptides, Peptidomimetics, and Polypeptides from Marine Sources: A Wealth of Natural Sources for Pharmaceutical Applications
- PMID: 28441741
- PMCID: PMC5408270
- DOI: 10.3390/md15040124
Peptides, Peptidomimetics, and Polypeptides from Marine Sources: A Wealth of Natural Sources for Pharmaceutical Applications
Abstract
Nature provides a variety of peptides that are expressed in most living species. Evolutionary pressure and natural selection have created and optimized these peptides to bind to receptors with high affinity. Hence, natural resources provide an abundant chemical space to be explored in peptide-based drug discovery. Marine peptides can be extracted by simple solvent extraction techniques. The advancement of analytical techniques has made it possible to obtain pure peptides from natural resources. Extracted peptides have been evaluated as possible therapeutic agents for a wide range of diseases, including antibacterial, antifungal, antidiabetic and anticancer activity as well as cardiovascular and neurotoxin activity. Although marine resources provide thousands of possible peptides, only a few peptides derived from marine sources have reached the pharmaceutical market. This review focuses on some of the peptides derived from marine sources in the past ten years and gives a brief review of those that are currently in clinical trials or on the market.
Keywords: antifungal peptides; antimicrobial peptides; extraction of peptides; marine peptides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
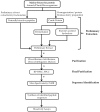
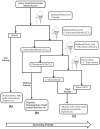
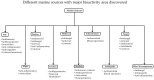
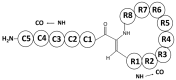



References
-
- Buchwald H., Dorman R.B., Rasmus N.F., Michalek V.N., Landvik N.M., Ikramuddin S. Effects on GLP-1, PYY, and leptin by direct stimulation of terminal ileum and cecum in humans: Implications for ileal transposition. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2014;10:780–786. doi: 10.1016/j.soard.2014.01.032. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

