[Effect of Nm23-H1 Nuclear Localization on Proliferation of Human Lung Adenocarcinoma Cell Line A549]
- PMID: 28442010
- PMCID: PMC5999672
- DOI: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2017.04.02
[Effect of Nm23-H1 Nuclear Localization on Proliferation of Human Lung Adenocarcinoma Cell Line A549]
Abstract
Background: Recent studies have indicated that Nm23-H1 is found in the nucleus, but previous studies have been based on the overexpression or suppression of Nm23-H1 in the cytoplasm. Due to the lacking nuclear localization signal of Nm23-H1, these results cannot reflect or repeat cells in which Nm23-H1 mainly positioned in nuclei and whether they cause clinical biological effects. Therefore, to explore the effects of transposing Nm23-H1 from the cytoplasm to the nucleus during lung cancer cell proliferation, a vector with a nuclear localization signal of Nm23-H1 was constructed and A549 cells were transfected.
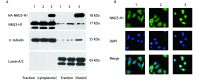
Methods: Gene recombination technology was used to construct pLentis-CMV-NME1-IRES2-PURO lentiviral vectors using a nuclear localization signal sequence, and the recombinant plasmid was verified using restriction enzyme analysis and sequencing. Nm23-H1 positioning and expression were performed after the stably transfected A549 cells were assessed by Western blot and confocal laser scanning microscope. The A549 cell proliferation was assessed using a cell counting kit-8. Flow cytometry was performed to assess the cell cycle distribution of A549 cells.
Results: The directional Nm23-H1 lentiviral vector was successfully constructed within the nucleus. Compared with that of the empty vector group, the proliferation rates of the transfection groups at 72 h, 96 h, and 120 h were remarkably increased (P<0.000,1). Moreover, the empty vector group of A549 cells in the G0/G1 phase proportion was 35.69%, which was higher than the 28.28% of the transfection group (t=1.461, P=0.217); furthermore, the transfection group of A549 cells in the G2/M phase proportion was 58.7% and that of the empty vector group was 31.30% (t=4.560, P=0.010).
Conclusions: Human lung adenocarcinoma cell line A549 cells of Nm23-H1 nuclear localized mainly in the G2/M phase and the nuclear Nm23-H1 promoted A549 cell proliferation in vitro.
背景与目的 现有研究发现Nm23-H1还存在胞核表达,而既往的研究都是以过表达或抑制胞浆Nm23-H1为研究手段,由于Nm23-H1本身缺乏核引导序列,其研究结果并不能真实反映或重复临床中Nm23-H1以胞核定位为主的实际生物学效应。因此,本研究通过构建带有核引导序列的Nm23-H1载体并转染A549细胞以探讨Nm23-H1从胞浆向胞核转位对肺癌细胞增殖的影响。方法 采用基因重组技术构建带核定位信号序列的pLentis-CMV-NME1-IRES2-PURO慢病毒载体,酶切和测序鉴定正确后,稳定转染A549细胞后用Western blot和激光共聚焦检测Nm23-H1蛋白的定位和表达,用CCK-8法检测细胞的增殖,流式细胞术检测细胞周期变化。结果 成功构建了核内定向表达Nm23-H1的慢病毒载体。转染组在72 h、96 h和120 h时增殖率与空载体组相比均显著升高(P<0.000,1)。空载体组A549细胞在G0期/G1期所占比例为35.69%,高于转染组的28.28%(t=1.461, P=0.217);而转染组细胞在G2期/M期所占比例为58.7%,空载体组为31.30%(t=4.560, P=0.010)。结论 Nm23-H1在人肺腺癌A549细胞的核内过表达使细胞主要分布在G2期/M期并促进了细胞的体外增殖。.
Figures




Similar articles
-
[nm23-H1-siRNA enhances the chemosensitivity to liposome-encapsulated paclitaxel in lung adenocarcinoma cells in vitro].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2011 Jun;33(6):405-9. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 21875478 Chinese.
-
[Establishment of the cell line that human lung adenocarcinoma can stably express luciferase which is absent of nm23-H1 expression and detecting its luminescence in vitro and in vivo].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2012 Mar;15(3):152-8. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2012.03.04. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 22429578 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
[Lentivirus-mediated stable silencing of nm23-H1 gene in lung cancer cells and the influence on biological behavior].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2012 Mar;15(3):139-45. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2012.03.02. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 22429576 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
The Nm23-H1-h-Prune complex in cellular physiology: a 'tip of the iceberg' protein network perspective.Mol Cell Biochem. 2009 Sep;329(1-2):149-59. doi: 10.1007/s11010-009-0115-4. Epub 2009 Apr 24. Mol Cell Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19390954 Review.
-
The case for extracellular Nm23-H1 as a driver of acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) progression.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2015 Feb;388(2):225-33. doi: 10.1007/s00210-014-1027-8. Epub 2014 Aug 15. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25119778 Review.
Cited by
-
Nm23-H1 is involved in the repair of ionizing radiation-induced DNA double-strand breaks in the A549 lung cancer cell line.BMC Cancer. 2018 Jul 3;18(1):710. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4592-2. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29970055 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear NME1 enhances the malignant behavior of A549 cells and impacts lung adenocarcinoma patient prognosis.iScience. 2024 Jun 15;27(7):110286. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110286. eCollection 2024 Jul 19. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39055952 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang Z, Liu H, Liu B, et al. Gene expression levels of CSNK1A1 and AAC-11, but not NME1, in tumor tissues as prognostic factors in NSCLC patients. Med Sci Monit. 2010;16(8):CR357–364. - PubMed
-
- Gazzeri S, Brambilla E, Negoescu A, et al. Overexpression of nucleoside diphosphate/kinase A/nm23-H1 protein in human lung tumors: association with tumor progression in squamous carcinoma. Lab Invest. 1996;74(1):158–167. - PubMed
-
- Zhang ZM. The interaction of APE1 and its related proteins inradiotherapy of human cancer. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/D160655 Chongqing: Third Military Medical University. 2011:57.
- 张 志敏. APE1作用相关蛋白及其在肿瘤放射治疗中的作用研究. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/D160655 重庆:第三军医大学. 2011:57.
-
- Salerno M, Palmieri D, Bouadis A, et al. Nm23-H1 metastasis suppressor expression level influences the binding properties, stability, and function of the kinase suppressor of Ras1 (KSR1) Erk scaffold in breast carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 2005;25(4):1379–1388. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.4.1379-1388.2005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

