Rapamycin modulation of p70 S6 kinase signaling inhibits Rift Valley fever virus pathogenesis
- PMID: 28442428
- PMCID: PMC5530372
- DOI: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2017.04.011
Rapamycin modulation of p70 S6 kinase signaling inhibits Rift Valley fever virus pathogenesis
Abstract
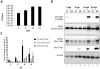
Despite over 60 years of research on antiviral drugs, very few are FDA approved to treat acute viral infections. Rift Valley fever virus (RVFV), an arthropod borne virus that causes hemorrhagic fever in severe cases, currently lacks effective treatments. Existing as obligate intracellular parasites, viruses have evolved to manipulate host cell signaling pathways to meet their replication needs. Specifically, translation modulation is often necessary for viruses to establish infection in their host. Here we demonstrated phosphorylation of p70 S6 kinase, S6 ribosomal protein, and eIF4G following RVFV infection in vitro through western blot analysis and in a mouse model of infection through reverse phase protein microarrays (RPPA). Inhibition of p70 S6 kinase through rapamycin treatment reduced viral titers in vitro and increased survival and mitigated clinical disease in RVFV challenged mice. Additionally, the phosphorylation of p70 S6 kinase was decreased following rapamycin treatment in vivo. Collectively these data demonstrate modulating p70 S6 kinase can be an effective antiviral strategy.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Abdel-Wahab KS, El Baz LM, El-Tayeb EM, Omar H, Ossman MA, Yasin W. Rift Valley Fever virus infections in Egypt: Pathological and virological findings in man. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72:392–396. - PubMed
-
- Al-Hazmi M, Ayoola EA, Abdurahman M, Banzal S, Ashraf J, El-Bushra A, Hazmi A, Abdullah M, Abbo H, Elamin A, Al-Sammani el T, Gadour M, Menon C, Hamza M, Rahim I, Hafez M, Jambavalikar M, Arishi H, Aqeel A. Epidemic Rift Valley fever in Saudi Arabia: a clinical study of severe illness in humans. Clin Infect Dis. 2003;36:245–252. - PubMed
-
- Alamo JM, Barrera L, Casado MD, Bernal C, Marin LM, Suarez G, Sanchez-Moreno L, Jimenez R, Suarez-Grau JM, Sousa JM, Cordero E, Gomez-Bravo MA. Efficacy, tolerance, and safety of mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors as rescue immunosuppressants in liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2009;41:2181–2183. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

