Effects of high-fat diet and fructose-rich diet on obesity, dyslipidemia and hyperglycemia in the WBN/Kob-Leprfa rat, a new model of type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 28442647
- PMCID: PMC5487803
- DOI: 10.1292/jvms.17-0136
Effects of high-fat diet and fructose-rich diet on obesity, dyslipidemia and hyperglycemia in the WBN/Kob-Leprfa rat, a new model of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
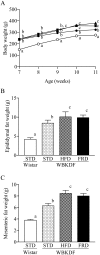
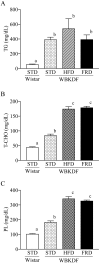
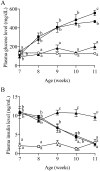
Obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) are occurring at epidemic-like rates, and these epidemics appear to have emerged largely from changes in daily diet. In the present study, we compared effects of high-fat diet (HFD) and fructose-rich diet (FRD) in WBN/Kob-Leprfa (WBKDF) rats that spontaneously develop obesity, dyslipidemia and T2DM. After a 4-week feeding of each diet, WBKDF-HFD and WBKDF-FRD rats exhibited aggravated obesity and dyslipidemia compared with WBKDF rats fed standard diet (STD). In contrast, hyperglycemia developed in WBKDF-STD rats was significantly inhibited in WBKDF-FRD rats, but not in WBKDF-HFD rats. The present study demonstrated that the 4-week feeding of HFD and FRD caused diet-induced obesity with a distinct phenotype in the glucose metabolism in WBKDF rats.
Keywords: WBN/Kob-Leprfa rat; diet-induced obesity; fructose-rich diet; high-fat diet; type 2 diabetes.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

