MicroRNA-30a Regulation of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Diabetic Cataracts Through Targeting SNAI1
- PMID: 28442786
- PMCID: PMC5430627
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-01320-3
MicroRNA-30a Regulation of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Diabetic Cataracts Through Targeting SNAI1
Abstract
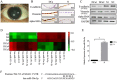
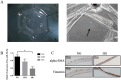
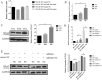
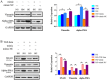
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is a highly conserved and fundamental process in development, fibrosis, and metastasis. During the process, epithelial cells lose their morphology and transcriptional program, and transdifferentiate to mesenchymal cells. It has been reported that lens epithelial cells undergo EMT during cataract formation, and regulation of microRNAs on genes is associated with lens development. However, the molecular mechanisms of this regulation in diabetic cataract still need to be investigated. In the present study, the expression of E-cadherin was downregulated, while the expression of alpha-SMA and vimentin was upregulated in diabetic cataract tissues and the in vitro model, suggesting the involvement of EMT in diabetic cataract formation. Results of miRNA profiling demonstrated that miR-30a was markedly downregulated in diabetic cataract tissues. Overexpression of miR-30a-5p decreased SNAI1, a known modulator of EMT, and the expression of vimentin and alpha-SMA in our diabetic cataract model in vitro. It is concluded that EMT is involved in human diabetic cataract, and upregulation of miR-30a can repress EMT through its targeting of SNAI1 in lens epithelial cells, which make miR-30a a novel target of therapeutic intervention for human diabetic cataract.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Worgul BV, Merriam GR, Jr., Medvedovsky C. Cortical cataract development–an expression of primary damage to the lens epithelium. Lens and eye toxicity research. 1989;6:559–571. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

