Effects of fitness training on physical fitness parameters and quality of life in human immunodeficiency virus-positive Indian females
- PMID: 28442803
- PMCID: PMC5389215
- DOI: 10.4103/0253-7184.196886
Effects of fitness training on physical fitness parameters and quality of life in human immunodeficiency virus-positive Indian females
Abstract
Purpose: Highly active antiretroviral therapy has significantly extended survival of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infected patients. These drugs suppress replication of HIV but at the same time, have many physical and mental side effects which may affect daily activities of the patients. The present study assessed if moderate intensity exercise program helped in enhancing the physical fitness and quality of life (QoL) in HIV positive females which may reduce the comorbidities associated with the disease and medications.
Aim and objectives: The aim of this study is to study the effects of moderate intensity physical training on physical fitness parameters and QoL in HIV positive females.
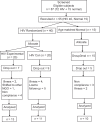
Methodology: Post IEC approval, a randomized control, single-blinded, parallel group trial was conducted on 55 females (20 experimental HIV, 20 control HIV, 15 control normal) matching the selection criteria. Post informed consent, their muscular endurance, flexibility, aerobic capacity, and QoL was assessed. Moderate intensity physical exercises were given to experimental HIV and control normal 5 days/week for 8 weeks and subjects were reassessed for above parameters. Intragroup analysis was performed using paired t-test while inter-group was by one-way ANOVA with alpha set at ≤0.05.
Results: Moderate-intensity exercises improved muscular endurance (P < 0.05), flexibility (P < 0.05), and aerobic capacity (P < 0.05)in experimental HIV and control normal group as compared to control HIV group. QoL in experimental HIV showed improvement in all the domains.
Conclusion: Moderate-intensity exercises help improve the physical fitness as well as enhance the QoL in HIV positive females.
Keywords: Endurance; VO2 max; human immunodeficiency virus; moderate intensity exercise; muscular strength; physical fitness; quality of life.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures







References
-
- UNAIDS Report on the Global AIDS Epidemic. 2013. [Last viewed on 2016 Jul 07]. Available from: http://www.files.unaids.org/en/media/unaids/contentassets/documents/epid... .
-
- Lakhashe S, Thakar M, Godbole S, Tripathy S, Paranjape R. HIV infection in India: Epidemiology, molecular epidemiology and pathogenesis. J Biosci. 2008;33:515–25. - PubMed
-
- UNAIDS and WHO Epidemiological Fact Sheet on HIV/AIDS and Sexually Transmitted Diseases (India) [Last viewed on 2016 Jul 07]. Available from: http://www.data.unaids.org/publications/fact-sheets01/india_en.pdf .
-
- Stanley S, Sethuramalingam V, Sathia S. Life Satisfaction and Pessimism in HIV positive people: A comparative study from India. Int J Psychosoc Rehabil. 2013;18:95–104.
-
- Stages of HIV. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. Revised 27 August, 2015. [Last viewed on 2016 Jul 07]. Available from: https://www.aids.gov/hiv-aids-basics/just-diagnosed-with-hiv-aids/hiv-in...
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

