Bioequivalence study of a new sildenafil 100 mg orodispersible film compared to the conventional film-coated 100 mg tablet administered to healthy male volunteers
- PMID: 28442892
- PMCID: PMC5395281
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S124034
Bioequivalence study of a new sildenafil 100 mg orodispersible film compared to the conventional film-coated 100 mg tablet administered to healthy male volunteers
Abstract
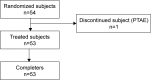
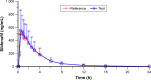
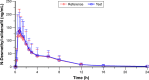
A new orodispersible film formulation of the phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor, sildenafil, has been developed to examine the advantages of an orally disintegrating film formulation and provide an alternative to the current marketed products for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. The pharmacokinetics of the sildenafil 100 mg orodispersible film (IBSA) was compared to that of the conventional marketed 100 mg film-coated tablet (Viagra®) after single-dose administration to 53 healthy male volunteers (aged 18-51 years) in a randomized, open, two-way crossover bioequivalence study. Each subject received a single oral dose of 100 mg of sildenafil as test or reference formulation administered under fasting conditions at each of the two study periods according to a randomized crossover design. There was a washout interval of ≥7 days between the two administrations of the investigational medicinal products. Blood samples for pharmacokinetic analysis were collected up to 24 h post-dosing. The primary objective was to compare the rate (peak plasma concentration; Cmax) and extent (area under the curve [AUC] from administration to last observed concentration time; AUC0-t) of sildenafil absorption after single-dose administration of test and reference. Secondary endpoints were observed to describe the plasma pharmacokinetic profiles of sildenafil and its metabolite N-desmethyl-sildenafil relative bioavailability and safety profile after single-dose administration. The mean sildenafil and N-desmethyl-sildenafil plasma concentration-time profiles up to 24 h after single-dose administration of sildenafil 100 mg orodispersible film and film-coated tablet were nearly superimposable. The bioequivalence test was fully satisfied for sildenafil and N-desmethyl-sildenafil in terms of rate and extent of bioavailability. Adverse events occurred at similar rates for the two formulations and were of mild-to-moderate severity. The results suggest that the new orodispersible film formulation can be used interchangeably with the conventional film-coated formulation.
Keywords: N-desmethyl-sildenafil; PDE5 inhibitor; bioequivalence; orodispersible film; pharmacokinetics; sildenafil.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure AG, IC, VF, and SR are IBSA employees. The other authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Hatzimouratidis K, Eardley I, Giuliano F, et al. Guidelines on male sexual dysfunction: erectile dysfunction and premature ejaculation. 2014. [Accessed June 20, 2016]. Available from: https://uroweb.org/guideline/male-sexual-dysfunction/ - PubMed
-
- Smith WB, 2nd, McCaslin IR, Gokce A, Mandava SH, Trost L, Hellstrom WJ. PDE5 inhibitors: considerations for preference and long-term adherence. Int J Clin Pract. 2013;67(8):768–780. - PubMed
-
- Limin M, Johnsen N, Hellstrom WJ. Avanafil, a new rapid-onset phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitor for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2010;19(11):1427–1437. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

