A review of drug delivery systems based on nanotechnology and green chemistry: green nanomedicine
- PMID: 28442906
- PMCID: PMC5396976
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S127683
A review of drug delivery systems based on nanotechnology and green chemistry: green nanomedicine
Abstract
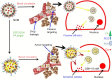
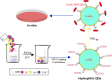
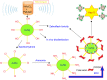
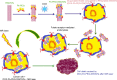
This review discusses the impact of green and environmentally safe chemistry on the field of nanotechnology-driven drug delivery in a new field termed "green nanomedicine". Studies have shown that among many examples of green nanotechnology-driven drug delivery systems, those receiving the greatest amount of attention include nanometal particles, polymers, and biological materials. Furthermore, green nanodrug delivery systems based on environmentally safe chemical reactions or using natural biomaterials (such as plant extracts and microorganisms) are now producing innovative materials revolutionizing the field. In this review, the use of green chemistry design, synthesis, and application principles and eco-friendly synthesis techniques with low side effects are discussed. The review ends with a description of key future efforts that must ensue for this field to continue to grow.
Keywords: cancer; drug delivery; green chemistry; nanoparticle.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



References
-
- Ravichandran S. Green chemistry- a potential tool for chemical synthesis. Int J Chem Tech Res. 2010;2(4):2188–2191.
-
- White MA, Johnson JA, Koberstein JT, Turro NJ. Toward the syntheses of universal ligands for metal oxide surfaces: controlling surface functionality through click chemistry. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128(35):11356–11357. - PubMed
-
- Arruebo M, Fernandez-Pacheco R, Ibarra MR, Santamaria J. Magnetic nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nano Today. 2007;2(3):22–32.
-
- Mornet S, Vasseur S, Grasset F, Duguet E. Magnetic nanoparticle design for medical diagnosis and therapy. J Mater Chem. 2004;14(21):61–75.
-
- Sun Z, Worden M, Thliveris JA, et al. Biodistribution of negatively charged iron oxide nanoparticles (IONPs) in mice and enhanced brain delivery using lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) Nanomedicine. 2016;12(7):1775–1784. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

