miR-762 can negatively regulate menin in ovarian cancer
- PMID: 28442921
- PMCID: PMC5396954
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S127872
miR-762 can negatively regulate menin in ovarian cancer
Abstract
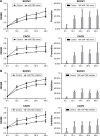
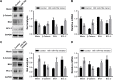
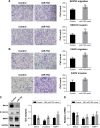
Ovarian cancer accounts for the major part of the mortality attributable to female reproductive system malignant tumors worldwide. Recently, the incidence of ovarian cancer has been increasing annually, and there remains a lack of suitable treatment methods that can significantly improve the 5-year survival rates of patients. Therefore, it is necessary to identify more effective treatments for ovarian cancer. It is established that microRNAs (miRNAs) have important roles in the diagnosis and treatment of ovarian cancer and a specific miRNA, miR-762, can promote the development of a variety of tumors. Menin is encoded by MEN1, a tumor suppressor gene, that is usually downregulated in ovarian cancer. In this study, we evaluated the expression levels of miR-762 and menin in ovarian cancer tissues and demonstrated that they were correlated. In addition, we found that miR-762 can downregulate the expression of menin through a binding site in its 3'-UTR and consequently upregulate the Wnt cell signaling pathway to promote the development of ovarian cancer. These results indicate that miR-762 is a promising potential target for the treatment of ovarian cancer.
Keywords: menin; miR-762; ovarian cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



References
-
- Latha TS, Panati K, Gowd DS, Reddy MC, Lomada D. Ovarian cancer biology and immunotherapy. Int Rev Immunol. 2014;33(5):428–440. - PubMed
-
- Nawaz M, Fatima F, Nazarenko I, et al. Extracellular vesicles in ovarian cancer: applications to tumor biology, immunotherapy and biomarker discovery. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2016;13(4):395–409. - PubMed
-
- Brouwer J, Kluiver J, de Almeida RC, et al. Small RNA sequencing reveals a comprehensive miRNA signature of BRCA1-associated high-grade serous ovarian cancer. J Clin Pathol. 2016 Apr;:5. Epub. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

