A Novel Long Non-coding RNA, durga Modulates Dendrite Density and Expression of kalirin in Zebrafish
- PMID: 28442991
- PMCID: PMC5385350
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2017.00095
A Novel Long Non-coding RNA, durga Modulates Dendrite Density and Expression of kalirin in Zebrafish
Abstract
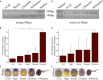
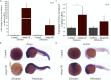
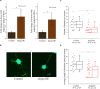
Kalirin, a key player in axonal development, nerve growth and synaptic re-modeling, is implicated in many pathological conditions like schizophrenia and autism-spectrum disorders. Alternative promoters and splicing lead to functionally distinct isoforms, but the post-transcriptional regulation of Kalirin has not been studied. Here, we report a novel non-coding RNA, which we name durga, arising from the first exon of kalirin a (kalrna) in the antisense orientation in zebrafish. The kalrna and durga transcripts are barely detectable during early development, but steadily increase by 24 hours post-fertilization (hpf) as the brain develops. Over-expression of durga in the zebrafish embryo led to an increase in kalrna expression. The morphology of the neurons cultured from durga injected embryos had significantly fewer and shorter dendrites. Although durga has no apparent sequence homolog in mammals, based on gene synteny, we found a non-coding RNA arising from the 5' end of the human Kalrn gene and expressed in the human neuronal cell line, SH-SY5Y. We propose that the zebrafish lncRNA durga maintains dendritic length and density through regulation of kalrna expression and this may have further implications in mammalian systems.
Keywords: Kalirin; dendritic morphology; long non-coding RNA; primary neuron culture; zebrafish.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A Novel Cis-Regulatory lncRNA, Kalnc2, Downregulates Kalrn Protein-Coding Transcripts in Mouse Neuronal Cells.Noncoding RNA. 2023 Jan 13;9(1):7. doi: 10.3390/ncrna9010007. Noncoding RNA. 2023. PMID: 36649036 Free PMC article.
-
KALRN: A central regulator of synaptic function and synaptopathies.Gene. 2021 Feb 5;768:145306. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.145306. Epub 2020 Nov 13. Gene. 2021. PMID: 33189799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and characterization of human KALRN mRNA and Kalirin protein isoforms.Cereb Cortex. 2024 Dec 3;34(12):bhae470. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhae470. Cereb Cortex. 2024. PMID: 39656879 Free PMC article.
-
Age-dependent increase in Kalirin-9 and Kalirin-12 transcripts in human orbitofrontal cortex.Eur J Neurosci. 2016 Oct;44(7):2483-2492. doi: 10.1111/ejn.13351. Epub 2016 Aug 18. Eur J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27471199 Free PMC article.
-
Kalirin, a multifunctional Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor, is necessary for maintenance of hippocampal pyramidal neuron dendrites and dendritic spines.J Neurosci. 2003 Nov 19;23(33):10593-603. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-33-10593.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 14627644 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Systematic Identification of Long Noncoding RNAs during Three Key Organogenesis Stages in Zebrafish.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 19;25(6):3440. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063440. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542412 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome profiling analysis of sex-based differentially expressed mRNAs and lncRNAs in the brains of mature zebrafish (Danio rerio).BMC Genomics. 2019 Nov 8;20(1):830. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6197-9. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31703616 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of coding-lncRNA gene co-expression network uncovers conserved functional lncRNAs in zebrafish.BMC Genomics. 2018 May 9;19(Suppl 2):112. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-4458-7. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29764394 Free PMC article.
-
Functional enrichment analysis based on long noncoding RNA associations.BMC Syst Biol. 2018 Apr 24;12(Suppl 4):45. doi: 10.1186/s12918-018-0571-0. BMC Syst Biol. 2018. PMID: 29745842 Free PMC article.
-
A long noncoding RNA cluster-based genomic locus maintains proper development and visual function.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Jul 9;47(12):6315-6329. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz444. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31127312 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alam M. R., Johnson R. C., Darlington D. N., Hand T. A., Mains R. E., Eipper B. A. (1997). Kalirin, a cytosolic protein with spectrin-like and GDP/GTP exchange factor-like domains that interacts with peptidylglycine α-amidating monooxygenase, an integral membrane peptide-processing enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 12667–12675. 10.1074/jbc.272.19.12667 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

