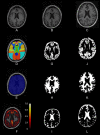
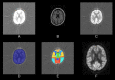
Pypes: Workflows for Processing Multimodal Neuroimaging Data
- PMID: 28443013
- PMCID: PMC5387693
- DOI: 10.3389/fninf.2017.00025
Pypes: Workflows for Processing Multimodal Neuroimaging Data
Keywords: MRI; PET; brain connectivity; brain imaging; denoising; image analysis; python; registration.
Figures

References
-
- Aiello M., Salvatore E., Cachia A., Pappatà S., Cavaliere C., Prinster A., et al. (2015). Relationship between simultaneously acquired resting-state regional cerebral glucose metabolism and functional MRI: a PET/MR hybrid scanner study. NeuroImage 113, 111–121. 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.03.01700022 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

