Deletion of Lipoteichoic Acid Synthase Impacts Expression of Genes Encoding Cell Surface Proteins in Lactobacillus acidophilus
- PMID: 28443071
- PMCID: PMC5387067
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00553
Deletion of Lipoteichoic Acid Synthase Impacts Expression of Genes Encoding Cell Surface Proteins in Lactobacillus acidophilus
Abstract
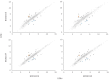
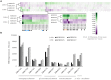
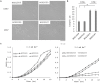
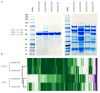
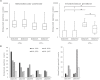
Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM is a well-characterized probiotic microorganism, supported by a decade of genomic and functional phenotypic investigations. L. acidophilus deficient in lipoteichoic acid (LTA), a major immunostimulant in Gram-positive bacteria, has been shown to shift immune system responses in animal disease models. However, the pleiotropic effects of removing LTA from the cell surface in lactobacilli are unknown. In this study, we surveyed the global transcriptional and extracellular protein profiles of two strains of L. acidophilus deficient in LTA. Twenty-four differentially expressed genes specific to the LTA-deficient strains were identified, including a predicted heavy metal resistance operon and several putative peptidoglycan hydrolases. Cell morphology and manganese sensitivity phenotypes were assessed in relation to the putative functions of differentially expressed genes. LTA-deficient L. acidophilus exhibited elongated cellular morphology and their growth was severely inhibited by elevated manganese concentrations. Exoproteomic surveys revealed distinct changes in the composition and relative abundances of several extracellular proteins and showed a bias of intracellular proteins in LTA-deficient strains of L. acidophilus. Taken together, these results elucidate the impact of ltaS deletion on the transcriptome and extracellular proteins of L. acidophilus, suggesting roles of LTA in cell morphology and ion homeostasis as a structural component of the Gram positive cell wall.
Keywords: Lactobacillus acidophilus; S-layer; cell surface; lipoteichoic acid; probiotic; proteomics; transcriptomics.
Figures
References
-
- Azcarate-Peril M. A., McAuliffe O., Altermann E., Lick S., Russell W. M., Klaenhammer T. R. (2005). Microarray analysis of a two-component regulatory system involved in acid resistance and proteolytic activity in Lactobacillus acidophilus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 71 5794–5804. 10.1128/AEM.71.10.5794-5804.2005 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

