Fine Mapping of a Resistance Gene RpsHN that Controls Phytophthora sojae Using Recombinant Inbred Lines and Secondary Populations
- PMID: 28443124
- PMCID: PMC5387331
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00538
Fine Mapping of a Resistance Gene RpsHN that Controls Phytophthora sojae Using Recombinant Inbred Lines and Secondary Populations
Abstract
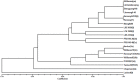
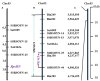
Phytophthora root rot (PRR), caused by Phytophthora sojae, has negative effects on soybean yield in China and can be controlled by identifying germplasm resources with resistance genes. In this study, the resistance locus RpsHN in the soybean line Meng8206 was mapped using two mapping populations. Initial mapping was realized using two recombinant inbred line (RIL) populations and included 103 F6:8 RILs derived from a cross of Meng8206 × Linhedafenqing, including 2600 bin markers, and 130 F6:8 RILs derived from a cross of Meng8206 × Zhengyang148, including 2267 bin markers. Subsequently, a 159 F2:3 secondary population derived from a cross of Meng8206 × Linmeng6-46, were used to fine map this locus using SSR markers. Finally, the resistance locus from Meng8206 was fine mapped to a 278.7 kb genomic region flanked by SSR markers SSRSOYN-25 and SSRSOYN-44 at a genetic distance of 1.6 and 1.0 cM on chromosome 3 (Chr. 03). Real-time RT-PCR analysis of the possible candidate genes showed that three genes (Glyma.03g04260, Glyma.03g04300, and Glyma.03g04340) are likely involved in PRR resistance. These results will serve as a basis for cloning, transferring of resistant genes and breeding of P. sojae-resistant soybean cultivars through marker-assisted selection.
Keywords: Phytophthora root rot; bins and SSR markers; fine mapping; linkage map; resistance gene; soybean.
Figures

References
-
- Athow K. L., Laviolette F. A., Mueller E. H., Wilcox J. R. (1980). A new major gene for resistance to Phytophthora megasperma var. sojae in soybean. Phytopathology 70 977–980. 10.1094/Phyto-70-977 - DOI
-
- Bernard R. L., Cremeens C. R. (1981). An allele at the rps1 locus from the variety ‘Kingwa’. Soybean Genet. Newsl. 8 40–42.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

